Electric current facts for kids
An electric current is like a river of tiny electric particles, called electric charge, flowing through something. Imagine electricity moving! We measure electric current in a unit called the ampere (A). You can find electric current in many places, like inside wires, in batteries that power your devices, and even in a flash of lightning!
How Electric Current Starts
In materials that conduct electricity well, like metals, some tiny particles called electrons are not held tightly by their atoms. These electrons can move around quite freely. Think of them as a cloud of tiny, speedy particles floating near the atoms.
When you connect a wire to a power source, like a battery, it creates an electric field. This field gives the loose electrons a gentle push, making them drift in one main direction. This steady drift of electrons is what we call electric current.
It's important to know that electric current isn't like a fast-moving river of electrons. The electrons themselves move quite slowly, only a few millimeters per second! However, the effect of the electric field travels very quickly, almost instantly. This is why a light bulb turns on right away when you flip a switch. It's more like a chain reaction where the push travels fast, even if the individual parts move slowly.
Current in Circuits
When electric current flows through a path, we call this path a circuit. Sometimes, we want to slow down the current or control it. This is where resistors come in. A resistor is a component that adds resistance to a circuit, which helps to slow down the flow of current.
The relationship between how much resistance there is, how much current flows, and the "push" from the power source (called voltage) is described by something called Ohm's law. This law helps engineers design circuits so that electricity flows just right for different devices.
Images for kids
-
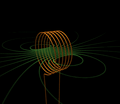
An electric current flowing through a coil of wire, called a solenoid, creates a magnetic field.
-
When the electric current in the solenoid changes, it creates a changing magnetic field. This changing field can make an electric current flow in a nearby wire loop. This is called electromagnetic induction.
See also
 In Spanish: Corriente eléctrica para niños
In Spanish: Corriente eléctrica para niños