Elongation facts for kids
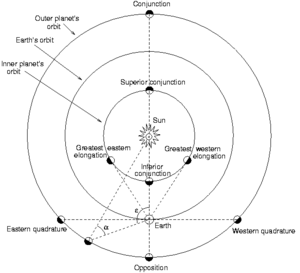
Elongation is a cool word used in astronomy. It describes the angle between the Sun and a planet, as we see it from Earth. Imagine drawing a line from Earth to the Sun, and another line from Earth to a planet. The angle between these two lines is the elongation!
What is Elongation?
Elongation helps us understand where planets are in the sky compared to the Sun. It's like measuring how far away a planet appears from the Sun.
Seeing Planets in the Sky
When we talk about planets like Mercury or Venus, which orbit closer to the Sun than Earth does, they are called inferior planets.
- When an inferior planet is visible right after sunset, it's near its greatest eastern elongation. This means it's as far east of the Sun as it can get from our view. It looks like it's "following" the Sun down.
- When an inferior planet is visible just before sunrise, it's near its greatest western elongation. This means it's as far west of the Sun as it can get. It looks like it's "leading" the Sun up.
For Mercury, this greatest angle can be between 18° and 28°. For Venus, it's much wider, between 45° and 47°.
Why the Angle Changes
You might wonder why these angles change. It's because the paths planets take around the Sun are not perfect circles. They are slightly stretched out, like an oval, which we call an elliptical orbit. Because of these oval shapes, the distance between a planet and the Sun changes a little bit, which also changes the angle we see from Earth.
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |