Venus facts for kids

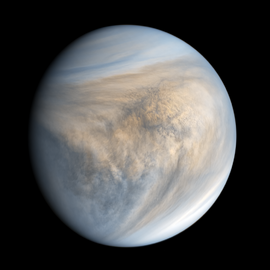
A picture of Venus made from images taken by the Mariner 10 space probe. The colors are adjusted to look like what a person might see. A thick layer of clouds always hides the surface.
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Named after
|
Roman | ||||||||||||||||
| Adjectives | Venusian rarely Cytherean or Venerean / Venerian | ||||||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics | |||||||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 0.728213 AU (108.94 million km) | ||||||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 0.718440 AU (107.48 million km) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.723332 AU (108.21 million km) | |||||||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.006772 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
| 583.92 days | |||||||||||||||||
|
Average orbital speed
|
35.02 km/s | ||||||||||||||||
| 50.115° | |||||||||||||||||
| Inclination |
|
||||||||||||||||
| 76.680° | |||||||||||||||||
| 54.884° | |||||||||||||||||
| Satellites | None | ||||||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics | |||||||||||||||||
|
Mean radius
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Volume |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Mass |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Mean density
|
5.243 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 8.87 m/s2 (0.904 g0) | |||||||||||||||||
| 10.36 km/s (6.44 mi/s) | |||||||||||||||||
| −116.75 d (retrograde) 1 Venus solar day |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Sidereal rotation period
|
−243.0226 d (retrograde) | ||||||||||||||||
|
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
1.81 m/s | ||||||||||||||||
| 2.64° (for retrograde rotation) 177.36° (to orbit) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
North pole right ascension
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
North pole declination
|
67.16° | ||||||||||||||||
| Albedo | |||||||||||||||||
| Temperature | 232 K (−41 °C) (blackbody temperature) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
| −4.92 to −2.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| −4.4 | |||||||||||||||||
| 9.7–66.0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Atmosphere | |||||||||||||||||
|
Surface pressure
|
93 bar (9.3 MPa) 92 atm |
||||||||||||||||
| Composition by volume |
|
||||||||||||||||
Venus is the second planet from the Sun and Earth's closest planetary neighbor. It is often called Earth's "sister" or "twin" because it is almost the same size and is made of similar rocky materials. However, Venus is a world of extremes and is very different from Earth.
Its atmosphere is thick and toxic, trapping heat and making it the hottest planet in the Solar System. From Earth, Venus is the brightest object in the night sky after the Sun and the Moon. It often appears as a brilliant "morning star" just before sunrise or an "evening star" just after sunset. Venus has no moons.
Contents
Physical characteristics
Venus is one of the four rocky planets in our Solar System, along with Mercury, Earth, and Mars. Its size and mass are very similar to Earth's. But the conditions on Venus are completely different.
The planet is covered by a thick atmosphere made mostly of carbon dioxide. This gas traps heat in a powerful greenhouse effect, which raises the surface temperature to an average of 464 °C (867 °F). That's hot enough to melt lead! The air pressure on the surface is also extreme—more than 90 times that of Earth's. This is like the pressure you would feel one kilometer deep in the ocean.
Surface and geography
Because of its thick clouds, we can't see the surface of Venus with a normal telescope. Scientists have used radar to map its surface from spacecraft. These maps show that about 80% of Venus is covered by smooth volcanic plains.
There are also two large highland areas that look like continents. The northern one is called Ishtar Terra and is about the size of Australia. It contains the highest mountain range on Venus, Maxwell Montes. The southern continent is called Aphrodite Terra, which is about the size of South America.
The surface of Venus is quite young, estimated to be between 300 and 600 million years old. This is because volcanoes have been very active, covering the older surface with fresh lava.
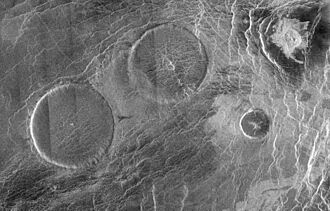
Volcanoes and craters
Venus has more volcanoes than any other planet in the Solar System—over 85,000 have been found! This doesn't mean it's more active than Earth, but its crust is older and doesn't get recycled the way Earth's does. Evidence from space probes suggests that some of these volcanoes may still be active today.
There are very few impact craters on Venus compared to planets like Mars or Mercury. This is because the thick atmosphere burns up smaller asteroids before they can reach the ground. The craters that do exist are in very good condition, which also suggests that the surface was completely reshaped by volcanic activity not too long ago.
Internal structure
Like Earth, Venus is thought to have a core, a mantle, and a crust. The core is likely made of metal and is probably at least partly liquid. However, unlike Earth, Venus does not seem to have plate tectonics. On Earth, the crust is broken into plates that move around, which helps the planet lose heat from its interior.
On Venus, the crust is thought to be too strong to break into plates. Instead, heat builds up inside the planet until it bursts out in massive volcanic events that resurface the entire planet. This could also be why Venus does not have a strong magnetic field like Earth does.
Atmosphere and climate
Venus has the thickest atmosphere of all the rocky planets. It is made of 96.5% carbon dioxide, which is the main reason for its runaway greenhouse effect. The planet is covered in clouds made not of water, but of droplets of sulfuric acid. These clouds are so thick that they reflect about 70% of the sunlight that hits them, which is why Venus appears so bright in our sky.
The winds at the top of the clouds are incredibly fast, reaching speeds of 300 km/h (185 mph). They blow the clouds all the way around the planet in just four Earth days. On the surface, however, the winds are very slow.
Because of the thick atmosphere, the temperature on Venus is almost the same everywhere, from the equator to the poles, and on both the day and night sides of the planet.
Orbit and rotation
Venus orbits the Sun every 224.7 Earth days. Its orbit is the most circular of any planet in the Solar System.
A day longer than a year
Venus has a very unusual rotation.
- It spins backwards. Most planets, including Earth, spin counter-clockwise. Venus spins clockwise. If you could stand on Venus, you would see the Sun rise in the west and set in the east.
- It spins very slowly. A single day on Venus (one full rotation) takes 243 Earth days. This is longer than its year! This means that on Venus, a day is longer than a year.
How to see Venus
Venus is easy to see without a telescope. Because its orbit is inside Earth's orbit, it always appears close to the Sun in the sky.
- When it is visible after sunset, it is called the Evening Star.
- When it is visible before sunrise, it is called the Morning Star.
Venus is so bright that it can sometimes be seen during the day if you know exactly where to look.
Phases of Venus
When viewed through a telescope, Venus shows phases just like our Moon. In 1610, Galileo Galilei was the first person to see these phases.
- When Venus is on the far side of the Sun, it looks small and "full."
- As it moves closer to Earth, it appears larger and looks like a "crescent."
Galileo's discovery was very important. It showed that Venus must be orbiting the Sun, not the Earth. This helped prove that the Earth was not the center of the universe.
Transits of Venus
A transit of Venus happens when the planet passes directly between the Sun and Earth. When this occurs, Venus can be seen as a small black dot moving across the face of the Sun.
Transits are very rare. They happen in pairs that are eight years apart, but these pairs are separated by more than 100 years. The last pair of transits happened in 2004 and 2012. The next one will not be until the year 2117.
Exploration of Venus
Because Venus is so close, it was one of the first planets to be visited by spacecraft.
- The first successful flyby was by NASA's Mariner 2 in 1962. It confirmed that Venus was extremely hot.
- The Soviet Union's Venera program sent many probes to Venus. In 1970, Venera 7 became the first spacecraft to successfully land on another planet and send back data. In 1975, Venera 9 sent back the first pictures from the surface.
- In the 1990s, NASA's Magellan orbiter used radar to create a detailed map of almost the entire surface of Venus.
Several missions are planned for the future. NASA plans to launch VERITAS and DAVINCI in the early 2030s to study the planet's surface and atmosphere.
Could there be life on Venus?
The surface of Venus is far too hot and harsh for life as we know it. However, some scientists think that life could exist high up in the clouds. About 50 km (30 miles) above the surface, the temperature and pressure are similar to Earth's.
In 2020, scientists announced they had detected a gas called phosphine in Venus's atmosphere. On Earth, this gas is usually produced by living things. This discovery caused a lot of excitement, but other studies have not been able to confirm it. The question of whether there is life in the clouds of Venus remains a mystery that future space missions hope to solve.
Venus in culture
Because it is so bright and easy to see, Venus has been known since ancient times. Many cultures gave it special importance.
- The ancient Babylonians knew it as the Star of Ishtar, their goddess of love and war.
- The ancient Greeks at first thought it was two different stars: Phosphorus in the morning and Hesperus in the evening. They later realized it was one object.
- The Romans named the planet after their goddess of love and beauty, Venus.
- The Maya civilization in Central America had a very advanced understanding of Venus's movements. They created detailed calendars based on its cycles.
The symbol for Venus (a circle with a cross below it) is used in science to represent the female gender.
See also
 In Spanish: Venus (planeta) para niños
In Spanish: Venus (planeta) para niños