Ethiopian civil conflict (2018–present) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Civil conflict in Ethiopia (2018–present) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the conflicts in the Horn of Africa | |||||||||
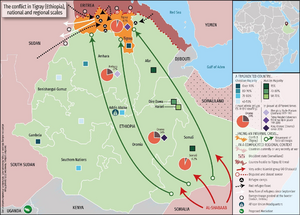
 Territorial control as of March 2023 Pro-federal government troops Ethiopian federal government and regional allies Eritrean Defence Forces Ethiopian federal government and Eritrean Defence Forces Anti-federal government rebels Tigray Defense Forces Oromo Liberation Army |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
Arms suppliers: |
|
||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Ali Diyaar Osman Abu Abdi Rahman |
|||||||||
| Units involved | |||||||||
| Unknown | |||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
8,000 captured 2 MiG-23 lost 2 Mi-35 lost 1 C-130 lost |
2,000 captured |
800+ killed, 100 captured (Ethiopian claim) | |||||||
| Hundreds of thousands killed, millions displaced | |||||||||
The civil conflicts in Ethiopia are ongoing fights that started when Abiy Ahmed became leader in 2018. Before this, Ethiopia had a main political group called the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front. When this group broke apart in 2018, tensions grew across the country.
Different groups, often based on ethnic background, began to attack soldiers and regular people. These attacks happened in many parts of Ethiopia. The situation got worse in November 2020 when a war started in the Tigray Region. This war was between the Ethiopian government and the local government in Tigray.
The Ethiopian National Defense Force (ENDF) and the Eritrean Defence Forces (EDF) entered Tigray. They took control of Mekelle, the capital city. However, the Tigray Defense Forces took back most of Tigray in mid-2021. They then joined forces with the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA) in late 2021. This new alliance also included seven smaller rebel groups. They called themselves the United Front of Ethiopian Federalist and Confederalist Forces.
Contents
Understanding the Conflict's Roots
Ethiopia has a long and complex history. Many of today's problems come from events that happened a long time ago. Understanding these past events helps us see why different groups are fighting now.
Early History and Land Control
Around 1889, Emperor Menelik II took control of new areas. These areas are now known as the Oromia, Sidama, and Somali Regions. He was from the Amhara group.
Reports from 1935 said that after Menelik's forces moved into these non-Abyssinian lands, people living there were enslaved. They also had to pay very high taxes. This led to many people leaving their homes.
Ethnic Differences and Rule
Later, during the time of Haile Selassie and the Derg government, some ethnic groups faced unfair treatment. These included Afars, Tigrayans, Eritreans, Somalis, and Oromos. The Amhara culture was often seen as the most important during these times.
Many Amhara people moved to southern Ethiopia. They worked in government, courts, and schools. In schools, the Oromo language was removed and replaced with Amharic. This made it harder for other cultures to keep their traditions.
Changes After the Derg Government
The Derg government fell in 1991. After this, Ethiopia had a short time of change before a new government started in 1995. Meles Zenawi became the prime minister. His government brought in a system called ethnic federalism. This system aimed to give more power to different ethnic regions.
However, this new system also led to more ethnic clashes. Some groups, like Amharas, Oromos, and Somalis, felt unfairly treated. At the same time, Tigrayan nationalism grew stronger. The Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) became very powerful.
Many people saw Meles's government as unfair. They believed it cheated in elections.
Abiy Ahmed's Leadership and New Tensions
In 2018, Abiy Ahmed became the new prime minister. He ended the old political group that the TPLF had led for 27 years. He started to change the country's politics. He even released some political prisoners.
But during his time as leader, violence between ethnic groups became much worse. By 2020, the relationship between Abiy's government and the TPLF was very bad. This led to the start of the Tigray War in November 2020.
Key Conflicts and Groups
The civil conflicts in Ethiopia involve several different groups and regions. Each conflict has its own reasons, but they are all connected to the larger issues in the country.
The Tigray War (2020–2022)
The Tigray War was a major conflict between the Ethiopian federal government and the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF). It started in November 2020. The fighting was very intense and caused a lot of damage.
The Ethiopian government worked with the Eritrean Defence Forces. They fought against the Tigray Defense Forces. In late 2022, a peace agreement was signed. This agreement aimed to stop the fighting in Tigray.
Oromo Conflict and OLA Insurgency
The Oromo conflict has been going on for a long time, since 1973. The Oromo Liberation Army (OLA) is a key group in this conflict. They are fighting against the government.
The OLA joined forces with the Tigray Defense Forces in 2021. They became part of the United Front of Ethiopian Federalist and Confederalist Forces. Peace talks between the government and the OLA started in April 2023.
Other Regional Conflicts
There have also been other conflicts in different regions:
- The Benishangul-Gumuz conflict (2019–2022)
- Fights involving the Somali State Resistance
- Conflicts with groups like the Agaw Liberation Front and the KDP
These conflicts often involve different ethnic groups fighting over land, resources, or political power.
Impact on People
The civil conflicts have had a very sad impact on the people of Ethiopia.
- Hundreds of thousands of people have been killed.
- Millions of people have been forced to leave their homes. They become displaced, meaning they have to move to other parts of the country.
- Many people do not have enough food or medical care because of the fighting.
These conflicts have made life very difficult for many families in Ethiopia.
Efforts for Peace
Despite the ongoing conflicts, there have been efforts to bring peace.
- A ceasefire was agreed between the Ethiopian government and some rebel groups.
- Peace talks have started with the Oromo Liberation Army.
These talks are important steps towards finding lasting solutions for the country.
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |