Giant star facts for kids
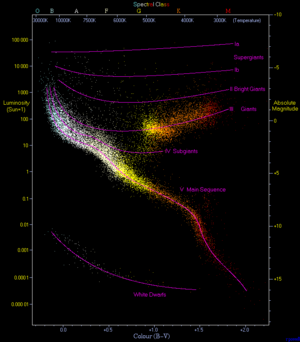
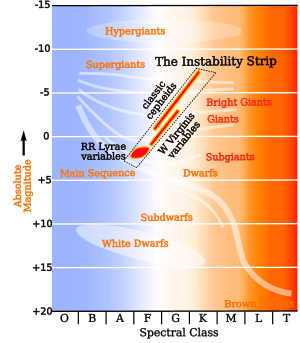
A giant star is a type of star that is much bigger and brighter than a typical main-sequence star of the same temperature. Think of them as the "grown-up" versions of stars, much larger than our own Sun.
Giant stars can be hundreds of times wider than the Sun. They also shine much brighter, from 10 to several thousand times more powerfully than the Sun. Because they are so big and bright, they use up their fuel faster, so they don't live as long as most main-sequence stars. Even bigger and brighter stars are called supergiants and hypergiants.
Sometimes, a very hot and bright main-sequence star might also be called a giant, even though it's still on the main sequence.
Contents
What Makes a Star a Giant?
Stars become giants when they run out of hydrogen fuel in their core. This is a normal part of a star's life cycle. When the hydrogen is gone, the star starts to fuse helium or other elements. This causes the star's outer layers to expand greatly, making it much larger and brighter.
How Big Are Giant Stars?
Giant stars are truly enormous. While our Sun has a diameter of about 1.4 million kilometers (870,000 miles), a giant star can be hundreds of times larger. For example, some red giants can be so big that if they replaced our Sun, their outer layers would reach past the orbit of Mars, or even Jupiter!
How Bright Are Giant Stars?
The brightness of a star is called its luminosity. Giant stars are very luminous. A typical giant star can be 10 to 1,000 times brighter than the Sun. Some of the brightest giants can even be several thousand times more luminous. This extreme brightness is why we can see some giant stars from very far away in space.
Types of Giant Stars
Astronomers classify giant stars into different types based on their temperature and color. Each type represents a different stage in a star's life or a different starting mass.
Red Giants
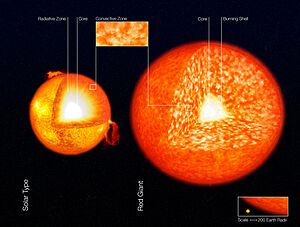
Red giants are the most common type of giant star. They are stars that have used up the hydrogen fuel in their core. This causes their outer layers to expand and cool down, making them appear reddish in color. Our Sun will become a red giant in about 5 billion years.
Yellow Giants
Yellow giants are stars that are hotter than red giants but cooler than blue giants. They are often in a transitional phase as they evolve. Some yellow giants are also known as Cepheid variables, which are stars that regularly change their brightness. These stars are very important for measuring distances in the universe.
Blue Giants
Blue giants are very hot and very bright stars. They are usually much more massive than the Sun. These stars are often young and still burning hydrogen in their cores, but their high mass makes them extremely luminous and large, so they are sometimes called giants. They have very short lives compared to smaller stars.
Subgiants and Bright Giants
- Subgiants are stars that are just starting to evolve off the main sequence. They are bigger and brighter than main-sequence stars but not yet as large as full giants.
- Bright giants are a class of stars that are brighter than normal giants but not quite as luminous as supergiants. They are often in a later stage of their evolution.
Images for kids
-
Internal structure of a Sun-like star and a red giant. ESO image.
See also
 In Spanish: Estrella gigante para niños
In Spanish: Estrella gigante para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |


