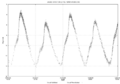Variable star facts for kids
A variable star is a star that changes how bright it looks from Earth. Most stars, like our Sun, stay pretty much the same brightness. But some stars can get much brighter or dimmer over time.
There are two main types of variable stars:
- Some stars seem to change brightness because something else is blocking their light. These are called extrinsic variable stars. Think of a solar eclipse where the Moon blocks the Sun's light. In space, this often happens in binary star systems, where two stars orbit each other and one star passes in front of the other.
- Other stars actually change their own brightness. These are called intrinsic variable stars. Their brightness changes because the star itself is getting bigger and smaller, or because of explosions on its surface.
Contents
Intrinsic Variable Stars
Intrinsic variable stars change their brightness because of what's happening inside them. Scientists group them into three main types:
- Pulsating variables: These stars expand and shrink in size, like a beating heart. This is part of their natural life cycle as they get older.
- Eruptive variables: These stars have sudden outbursts on their surfaces, like flares or giant bursts of gas.
- Cataclysmic or explosive variables: These stars go through huge, sudden changes, like a nova (a sudden brightening) or a supernova (a massive explosion).
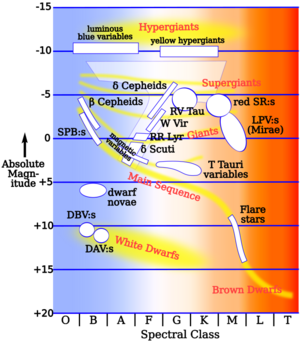
Pulsating Variable Stars
Pulsating stars change their brightness in a regular way. Their outer layers expand and contract, making them appear brighter and dimmer.
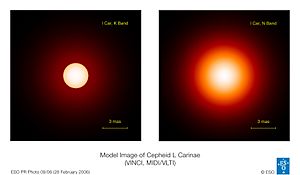
Cepheid Stars
Cepheid stars are very important because astronomers use them to measure distances in space. They have a special relationship between how long it takes for them to get brighter and dimmer (their period) and how truly bright they are.
- Some famous classical Cepheids include Delta Cephei (the first one discovered) and Polaris, also known as the North Star. Polaris is the closest classical Cepheid, but it's a bit unusual.
- Other types include Type II Cepheids and Dwarf Cepheids.
- RR Lyrae variables are another common type of pulsating star. They are often found in groups of stars called globular clusters and are also used to measure distances.
Long Period and Semi-Regular Stars
- Mira is a good example of a star that pulsates over a very long time, often more than 100 days. These stars are red giants, which are very old stars that have expanded greatly. In a few million years, they will shed their outer layers and become tiny, dense stars called white dwarfs.
Eruptive Variable Stars
Eruptive variable stars have sudden, unpredictable changes in brightness due to events on their surfaces.
Protostars
Protostars are very young stars that are still forming from clouds of gas and dust. They often show irregular changes in brightness as they gather more material and settle down.
Giants and Supergiants
Very large stars, like giants and supergiants, can easily lose parts of their outer layers. This can cause them to change brightness due to eruptions and bursts of gas leaving their surfaces.
Cataclysmic or Explosive Stars
These stars experience the most dramatic changes in brightness, often involving huge explosions.
Supernovae
Supernovae are among the most powerful explosions in the universe. A single supernova can briefly shine as brightly as an entire galaxy! This means they become over one hundred million times brighter than before.
Supernovae happen when a very massive star dies, or when a white dwarf star in a binary system pulls too much material from its companion star.
- When a massive star runs out of fuel, its core collapses very quickly. This collapse creates a huge shockwave that causes the star to explode, throwing its outer layers into space at incredible speeds.
- The exploding star's material can form beautiful clouds called supernova remnants. A famous example is the Crab Nebula, which was seen exploding by people in China and North America in the year 1054.
- After the explosion, the star's core might become a super-dense neutron star (often a pulsar) or even disappear completely.
Sometimes, a white dwarf star in a double star system can also cause a supernova. If it pulls too much gas from its partner star, it can become unstable and explode. These types of supernovae are very useful for astronomers to figure out how far away other galaxies are. One well-studied supernova of this type is SN 1987A, which happened in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
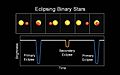
Eclipsing Variable Stars
Eclipsing variable stars are a type of extrinsic variable star. Their brightness changes because one star in a binary system passes in front of the other, blocking its light from our view.
- Algol is a very famous eclipsing binary star.
- Other examples include β Lyrae and W Ursae Majoris.
Images for kids
-
The Trifid Nebula contains Cepheid variable stars
-
Light curve of Mira variable χ Cygni
-
A photogenic variable star, Eta Carinae, embedded in the Carina Nebula
-
Images showing the expansion of the light echo of V838 Monocerotis
-
How eclipsing binaries vary in brightness
See also
 In Spanish: Estrella variable para niños
In Spanish: Estrella variable para niños