Solar eclipse facts for kids

A solar eclipse (say "ee-klips") happens when the Moon passes right between the Earth and the Sun. This makes the Moon block the Sun, either completely or partly. Solar eclipses can only happen during a new moon.
About two solar eclipses happen every year. Sometimes, there can even be five in one year! However, only two of these can be total solar eclipses. Total eclipses are quite rare and special to see.
A total eclipse is only visible from a small area on Earth. It lasts only a few minutes. Outside this narrow path, the eclipse will be partial, or not visible at all. Scientists can predict these paths many years ahead of time. Many people, called "eclipse chasers" or "umbraphiles" (because the Moon's shadow is called an umbra), travel far to see total solar eclipses. After a big eclipse in Europe in 1999, more people became interested in them.
Between two and five solar eclipses happen each year. At least one occurs during each eclipse season. Since 1582, years with five solar eclipses include 1693, 1758, 1805, 1823, 1870, and 1935. The next time this will happen is in 2206. On average, there are about 240 solar eclipses every 100 years.
A total solar eclipse is a natural phenomenon (a natural event). Long ago, some people thought eclipses happened because of magic. They also thought eclipses were a sign that something bad was going to happen. Some cultures still believe this today. A total solar eclipse can frighten people who don't know what it is. This is because the Sun seems to vanish during the day. The sky turns dark in just a few minutes.
Solar eclipses happen somewhere on Earth almost every year. Very similar eclipses happen every 18 years and 11.3 days. This repeating pattern is called the Saros cycle.
Contents
Past Solar Eclipses

The oldest recorded solar eclipse was found on a clay tablet in Ugarit, which is in modern Syria. It likely happened on May 3, 1375 BC, or March 5, 1223 BC. Another important eclipse was mentioned in an Assyrian text from June 15, 763 BC. This helps historians understand the timeline of the ancient Near East.
There are stories of even older eclipses. A Chinese king named Zhong Kang supposedly had two astronomers, Hsi and Ho, beheaded. They failed to predict an eclipse about 4,000 years ago. The earliest known drawing of a partial solar eclipse is from 1143 BCE. It might be found in the tomb of Ramses V and Ramses VI.

People in ancient times often saw eclipses as omens, or signs of future events. The ancient Greek historian Herodotus wrote about Thales of Miletus. Thales supposedly predicted an eclipse that happened during a battle between the Medes and the Lydians. Both armies stopped fighting and made peace because of the eclipse. This eclipse might have happened on May 28, 585 BC.
Chinese records of eclipses began around 720 BC. A Chinese astronomer named Shi Shen in the 4th century BC described how to predict eclipses. He used the positions of the Moon and Sun.
Some people have tried to figure out the exact date of Good Friday. They thought the darkness described during Jesus's crucifixion was a solar eclipse. However, this research has not been proven. Good Friday happens during Passover, which is at the time of a full moon. Solar eclipses only happen during a new moon. Also, the darkness lasted for three hours. A total solar eclipse only lasts for about eight minutes at most.
Types of Solar Eclipses
There are four main types of solar eclipses:
- A total eclipse is when the Sun is completely hidden behind the Moon. The Moon's dark shadow covers the Sun's bright surface. This makes the Sun's outer atmosphere, called the corona, easy to see.
- An annular eclipse is when the Sun is directly behind the Moon. But the Moon looks smaller than the Sun. This makes the Sun appear as a very bright ring, or annulus, around the Moon's shape.
- A hybrid eclipse (also called annular/total eclipse) is rare. It looks like a total eclipse in some parts of the Earth. In other parts, it looks like an annular eclipse.
- A partial eclipse is when the Moon is not exactly between the Sun and Earth. So, it does not hide the Sun completely. This type of eclipse can usually be seen from a large part of the Earth.
The Sun is about 400 times farther from Earth than the Moon is. The Sun's diameter is also about 400 times bigger than the Moon's. This is why the Sun and Moon look about the same size from Earth.
Looking at a Solar Eclipse Safely
Looking directly at the bright surface of the Sun can seriously hurt the retina of your eye. This is because of the strong radiation from the Sun. It can even cause blindness. Your retina does not feel pain, so you might not notice the damage for hours.
The Sun is usually so bright that it's hard to look at it directly. But when the Sun is covered during an eclipse, it's easier to stare. Looking at the Sun during an eclipse is just as dangerous. The only safe time is the very short period when the Sun's bright surface is completely covered during a total eclipse.
Looking at the Sun through binoculars, a telescope, or even a camera is extremely dangerous. It can damage your eye in less than a second.
Normally, when you look at the Sun, the pupil in your eye closes. This makes things darker and protects your eye. But if the Sun is almost completely covered during an eclipse, your pupil opens wide because there isn't as much light. However, the parts of the Sun that are still visible are still very bright. They can cause a lot of harm to your eye. Always use special eclipse glasses or viewers to look at any part of a solar eclipse!
Eclipse Chasing
A special group of people called "eclipse chasers" love to travel the world to see solar eclipses. These people are also known as umbraphiles, which means "shadow lovers." Umbraphiles travel to where eclipses will happen. They use special tools like solar viewing glasses (also called eclipse glasses) and telescopes to safely watch the Sun.
Photographing an Eclipse
You can photograph an eclipse with common camera gear. To see the Sun or Moon clearly, you need a long focus lens (at least 200 mm for a 35 mm camera). To make the Sun fill most of the picture, you need an even longer lens (over 500 mm).
Just like looking directly at the Sun, looking through a camera's viewfinder can harm your eye. So, be very careful! You need special solar filters for digital cameras. Even if you use a camera's live view screen, the Sun's rays can damage the camera's sensor if the lens isn't covered by a proper solar filter.
Recent and Future Solar Eclipses
Eclipses only happen during an eclipse season. This is when the Sun is close to a special point in the Moon's orbit called a node. Each eclipse is separated by one, five, or six lunations (which are like months based on the Moon). The middle of each season is 173.3 days apart. This is how long it takes the Sun to move from one node to the next.
Because of how the Moon's orbit works, similar eclipses happen again about every 18 years and 11.3 days. This period is called a saros. Each saros cycle starts with the Moon's shadow crossing Earth near one of the poles. Then, later eclipses in that cycle move towards the other pole. Eventually, the Moon's shadow misses Earth, and the cycle ends. Saros cycles have numbers; cycles 117 to 156 are active right now.
2022–2025
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
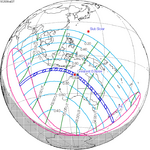
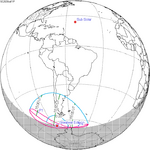
119 Partial from CTIO, Chile |
2022 April 30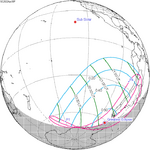 Partial |
−1.19008 | 124 Partial from Saratov, Russia |
2022 October 25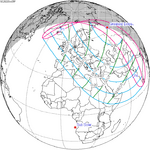 Partial |
1.07014 | |
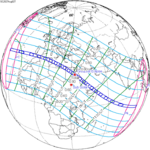
129 Total from East Timor |
2023 April 20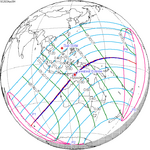 Hybrid |
−0.39515 | 134 Annular from Campeche, Mexico |
2023 October 14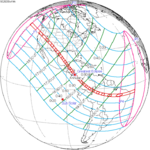 Annular |
0.37534 | |
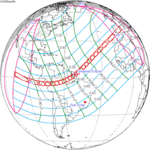
| 139 | 2024 April 8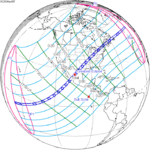 Total |
0.34314 | 144 | 2024 October 2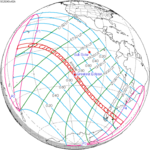 Annular |
−0.35087 | |
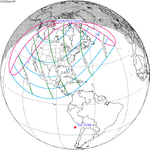
| 149 | 2025 March 29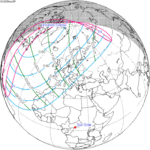 Partial |
1.04053 | 154 | 2025 September 21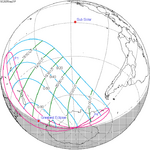 Partial |
−1.06509 | |
2026–2029
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
Partial solar eclipses on June 12, 2029, and December 5, 2029, occur in the next lunar year eclipse set.
Images for kids
-
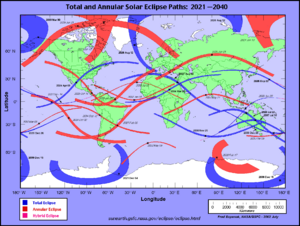
Total solar eclipse paths: 1001–2000, showing that total solar eclipses occur almost everywhere on Earth. This image was made from 50 separate images from NASA.
-
The progression of a solar eclipse on August 1, 2008 in Novosibirsk, Russia. The time between each picture is three minutes.
-
Eddington's original photograph of the 1919 eclipse. This picture helped prove Einstein's theory of general relativity.
See also
 In Spanish: Eclipse solar para niños
In Spanish: Eclipse solar para niños
 | Frances Mary Albrier |
 | Whitney Young |
 | Muhammad Ali |