Saros cycle facts for kids
The Saros cycle is a special pattern that helps us predict when eclipses will happen. It lasts for about 18 years, 11 days, and 8 hours. That's roughly 6585 and a third days!
What's cool about the Saros cycle is that after one full cycle, the Earth, Moon, and Sun all line up in almost the exact same way they did 18 years before. This means if there was a solar eclipse today, there will be a very similar one about 18 years from now. People in Ancient Greece were some of the first to figure out this pattern and use it to predict eclipses.
Contents
What is an Eclipse Cycle?
An eclipse happens when one space object blocks the light from another. For us on Earth, the most common eclipses are solar eclipses and lunar eclipses.
- A solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, blocking the Sun's light.
- A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth passes between the Sun and Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon.
These events don't happen every month because the Moon's orbit around Earth is tilted. The Saros cycle helps us understand when these alignments will repeat.
Why Does the Saros Cycle Work?
The Saros cycle works because three different cycles of the Moon's orbit almost perfectly match up after about 18 years. Let's look at them:
Moon's Orbit Around Earth
The Moon goes around the Earth, and the Earth goes around the Sun. For an eclipse to happen, the Sun, Earth, and Moon need to be in a straight line.
- Synodic Month: This is how long it takes for the Moon to go from one new moon to the next (about 29.5 days). This is important for solar eclipses.
- Draconic Month: This is how long it takes for the Moon to pass through the same "node" in its orbit (about 27.2 days). Nodes are the two points where the Moon's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit around the Sun. Eclipses can only happen when the Moon is near a node.
- Anomalistic Month: This is how long it takes for the Moon to go from its closest point to Earth (perigee) and back again (about 27.5 days). This affects how big an eclipse looks.
After 223 synodic months, 242 draconic months, and 239 anomalistic months, all three cycles line up again. This is why the Saros cycle is so good at predicting eclipses!
History of the Saros Cycle
People have been observing and predicting eclipses for thousands of years.
Ancient Observations
Ancient civilizations, like the Babylonians and the Greeks, were very good at watching the sky. They noticed patterns in the movement of the Sun, Moon, and stars.
- The Babylonians, around 700 BC, were among the first to discover the Saros cycle. They kept detailed records of eclipses.
- Greek philosophers, like Thales of Miletus, are said to have used this knowledge to predict eclipses.
Modern Predictions
Today, scientists use computers and very precise measurements to predict eclipses. However, the basic idea of the Saros cycle is still a key part of how they do it. It helps them understand the long-term patterns of eclipses.
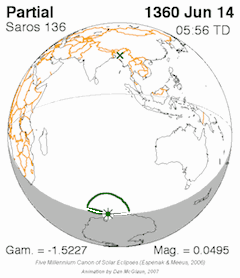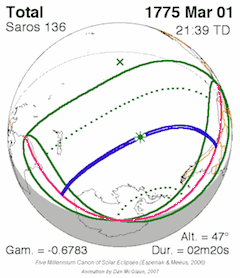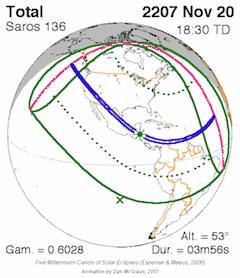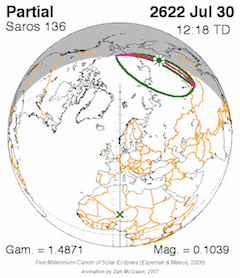
Different Saros Series
There isn't just one Saros cycle; there are many different "Saros series." Each series is like a family of eclipses that are related to each other.
- A Saros series starts with a very small eclipse, often near one of Earth's poles.
- Over many cycles (hundreds of years), the eclipses in that series gradually shift across the Earth.
- Eventually, the series ends with another small eclipse near the opposite pole.
Each Saros series lasts for about 1200 to 1500 years and includes about 70 to 85 eclipses.
Why is the Saros Cycle Important?
The Saros cycle is important for several reasons:
- Predicting Eclipses: It allows us to know exactly when and where future eclipses will occur. This is useful for scientists, astronomers, and even people who just want to watch these amazing events.
- Understanding Orbits: It helps us understand the complex movements of the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
- Historical Records: Ancient eclipse records, understood through the Saros cycle, help historians date past events.
The Saros cycle shows us how predictable and amazing the universe can be!
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Saros para niños
In Spanish: Saros para niños
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |