Glaciation facts for kids
Glaciation is when huge amounts of ice, called glaciers, form on land. These glaciers grow very large and cover big parts of the Earth. This process is often linked to something called the Milankovich theory, which explains how Earth's movements in space can cause big climate changes.
Contents
Glaciation: Earth's Ice Ages
What is Glaciation?
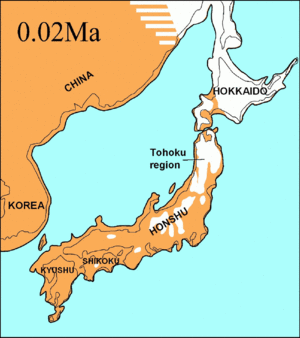
Glaciation is the process where ice sheets and glaciers expand across continents. When this happens, we call it an ice age. During an ice age, the Earth's climate gets much colder. Large areas that are usually free of ice become covered in thick layers of snow and ice. This can change landscapes and affect life on Earth.
Why Do Ice Ages Happen?
Ice ages are caused by a mix of different factors. These factors work together to make the Earth's climate much colder. They allow snow and ice to build up over thousands of years. Scientists study these causes to understand our planet's past and future.
How Temperature Changes
One main reason for glaciation is a drop in global temperatures. The average temperature around the world can fall by about 4 to 5 degrees Celsius. This might not sound like much, but it's enough to make a big difference. Colder temperatures mean that snow doesn't melt as easily in the summer. This allows it to build up year after year.
Snow and Ice Build-Up
Another important factor is how much snow falls, especially near the Arctic and Antarctica. If there's a lot of snow, and it doesn't melt completely in the warmer months, it starts to pile up. Over time, this snow gets compressed and turns into solid ice, forming glaciers. These glaciers then slowly spread out across the land.
Earth's Wobbly Orbit
The way Earth moves around the Sun isn't always the same. Sometimes, Earth's path, or orbit, is more like a perfect circle. Other times, it's more stretched out, like an oval. This change in shape affects how much sunlight reaches Earth. When Earth's orbit is more oval, some parts of the planet get less sun, leading to colder periods. This is part of the Milankovich theory.
Earth's Tilted Axis
Earth also spins on an imaginary line called its axis. This axis is tilted, which gives us seasons. But the amount of this tilt changes over very long periods. Sometimes, the tilt is greater, and other times it's less. When the tilt is smaller, the poles get less direct sunlight in summer. This means snow and ice can survive and grow, helping glaciers form.
Images for kids
-
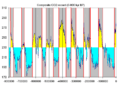
Glacial and interglacial cycles shown by CO2 levels. These levels are measured from ice core samples going back 800,000 years.
 | Leon Lynch |
 | Milton P. Webster |
 | Ferdinand Smith |