Gravitational energy facts for kids
Gravitational energy is a type of potential energy. It's the energy an object has because of its position, especially its height. Think of it as stored energy linked to gravity. For example, a book held high above the floor has more gravitational energy than the same book sitting on the floor. This energy is measured in units called Joules (J).
An object gains gravitational potential energy when it moves higher. The energy used to lift it changes into this stored energy. When the object moves back down, this stored energy turns into kinetic energy (movement). This is why riding a bike up a steep hill is hard. But coming down, you might not need to pedal. You are powered by the gravitational energy you stored going up! Gravitational energy also helps keep Earth and other planets orbiting the Sun.
How to Calculate Gravitational Energy
Scientists use a special formula to figure out how much gravitational potential energy an object has.
The formula looks like this: Gravitational potential energy = 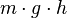
Let's break down what each letter means:
- m stands for the mass of the object. This is how much "stuff" the object is made of.
- g stands for the gravitational acceleration. This is how fast gravity pulls things down.
- h stands for the height of the object. This is how high it is above a certain point.
Units of Measurement
To use the formula correctly, scientists and students use specific units for each part:
- The mass (m) is measured in kilograms (kg).
- The height (h) is measured in metres (m).
- The gravitational acceleration (g) is a special number. On Earth, it's about 9.81 metres per second squared. This is known as the gravitational constant.
- When you use these units, the answer for gravitational potential energy will be in Joules (J).
Example Calculation
Let's imagine an object with a mass of 1.5 kilograms. It is held 2.5 metres above the ground.
To find its gravitational potential energy, we use the formula: 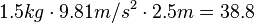 joules.
joules.
So, this object has 38.8 joules of gravitational potential energy.
See also

- In Spanish: Energía gravitatoria para niños

