Great Observatories program facts for kids
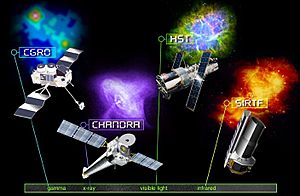
The Great Observatories program is a special group of four very powerful telescopes that orbit Earth in space. These amazing satellites were launched by NASA to help us learn more about the universe. Each of these space observatories sees a different kind of light, giving scientists a full picture of what's happening far away in space. They have all been super important for astronomy, which is the study of everything outside Earth's atmosphere.
Contents
Hubble Space Telescope (HST)
The Hubble Space Telescope (often called Hubble) is one of the most famous telescopes. It was launched into space in 1990. Hubble mainly looks at visible light, which is the light our eyes can see. It also sees ultraviolet light (which is like the light that causes sunburns) and near-infrared light (which is like heat).
In 1997, scientists added the ability for Hubble to see near-infrared light. There was also a special mission in 2009 to fix and upgrade Hubble, making it even better at exploring the cosmos.
Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO)
The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) was launched in 1991. This telescope was designed to look at the most energetic kind of light: gamma rays. It could also see some very strong X-rays.
Compton helped scientists study powerful events in space, like exploding stars and black holes. After nine years of amazing discoveries, the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory was safely brought back to Earth in 2000.
Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO)
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO) was launched in 1999. Chandra is special because it looks at soft X-rays. X-rays are a type of light that comes from very hot and energetic places in space, like supernovas and galaxy clusters.
Chandra's super-sharp vision helps scientists understand how these extreme environments work. It has given us incredible images of black holes, exploding stars, and distant galaxies.
Spitzer Space Telescope (SST)
The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST) was launched in 2003. Spitzer was designed to see infrared light. Infrared light is like heat, and it can pass through dusty clouds in space that block visible light.
By seeing in infrared, Spitzer allowed scientists to look inside cosmic dust clouds where new stars and planets are forming. It also helped us study distant galaxies and learn about the early universe.
Images for kids
-
Chandra, Hubble, and Spitzer composite image of the Crab Nebula (2009)
See also
 In Spanish: Grandes Observatorios para niños
In Spanish: Grandes Observatorios para niños