Nitrocellulose facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Nitrocellulose |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Other names | Cellulose nitrate; Flash paper; Flash cotton; Flash string; Gun cotton; Collodion; Pyroxylin |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | |
| Molar mass | 0 g mol-1 |
| Appearance | Yellowish white cotton-like filaments |
| Melting point | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 |
|
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
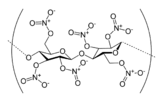
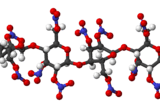
Nitrocellulose is a special material that catches fire very easily. You might also hear it called cellulose nitrate or flash paper. It's made by treating cellulose (which comes from plants, like cotton) with a strong chemical called nitric acid.
When nitrocellulose is used in propellants (like in bullets) or as a mild explosive, it's known as guncotton. It can also be made softer and more flexible by adding a substance like camphor.
For many years, companies like Kodak used this softer nitrocellulose to make film base for photographs, X-ray films, and even movies. This was called nitrate film. However, nitrate film was very unstable and caused many fires. Because of these dangers, a safer type of film called safety film began to be used. It replaced X-ray film in the 1930s and movie film by 1948.
Contents
What is Nitrocellulose?
Nitrocellulose is a type of polymer, which means it's made of many small units linked together. It starts from cellulose, a natural material found in plant cell walls, like in cotton or wood. To make nitrocellulose, cellulose is mixed with nitric acid or other strong chemicals. This process is called nitration. It changes the cellulose into a new substance that is highly flammable.
How Nitrocellulose is Used
Nitrocellulose has been used for many different things throughout history.
In Explosives and Propellants
One of its most famous uses is as guncotton. This form of nitrocellulose burns very quickly and powerfully. It was used as an explosive and as a propellant in firearms and artillery shells. Before guncotton, black powder was commonly used, but guncotton was much more powerful and produced less smoke.
In Photography and Film
For many years, nitrocellulose was the main material for making photographic and motion picture films.
- Early Films: From the late 1800s, nitrocellulose film allowed for the creation of movies and X-rays. It was strong and clear, making it perfect for capturing images.
- The Danger: The big problem with nitrate film was its flammability. It could catch fire very easily, even from a small spark or heat. Once it started burning, it was very hard to put out. It also broke down over time, becoming sticky and giving off dangerous gases.
- Switch to Safety Film: Because of the many fires and dangers, a new type of film called "safety film" was developed. This film was made from materials that were much less flammable. By the mid-20th century, safety film had completely replaced nitrate film for most uses.
Other Uses
Nitrocellulose is also used in other products:
- Lacquers and Coatings: It can be dissolved to make lacquers, which are clear coatings used to protect wood or metal.
- Celluloid: When mixed with camphor, nitrocellulose forms a plastic called celluloid. Celluloid was one of the first plastics and was used to make items like table tennis balls, combs, and early doll parts.
Safety and Handling
Because nitrocellulose is so flammable, it must be handled with great care. Old nitrate films, for example, are often stored in special, cool, and dry vaults to prevent them from catching fire or decaying. Modern materials have replaced nitrocellulose in many applications where safety is a concern.
Images for kids
-
Jam tin grenades were made in World War I using gun cotton
-
Table tennis ball, prepared from nitrocellulose (Celluloid)
See also
In Spanish: Nitrato de celulosa para niños