HMS Dragon (1647) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids History |
|
|---|---|
| Name | Dragon |
| Ordered | 9 January 1647 |
| Builder | Henry Goddard, Chatham Dockyard |
| Launched | 1650 |
| Commissioned | 1650 |
| Honours and awards |
|
| Name | HMS Dragon |
| Acquired | May 1660 |
| Honours and awards |
|
| Acquired | 1707 Act of Union |
| Fate | Wrecked, 16 March 1712 |
| General characteristics as built | |
| Class and type | 38-gun fourth rate |
| Tons burthen | 414+72⁄94 bm |
| Length |
|
| Beam | 28 ft 6 in (8.7 m) |
| Depth of hold | 14 ft 3 in (4.3 m) |
| Sail plan | ship-rigged |
| Complement |
|
| Armament |
|
| General characteristics after 1689-90 rebuild | |
| Class and type | 46-gun fourth rate ship of the line |
| Tons burthen | 530+79⁄94 bm |
| Length |
|
| Beam | 31 ft 9 in (9.7 m) |
| Depth of hold | 12 ft 2 in (3.7 m) |
| Sail plan | ship-rigged |
| Complement | 220 |
| Armament |
|
| General characteristics after 1707 rebuild | |
| Class and type | 46-54-gun fourth rate |
| Tons burthen | 719+73⁄94 tons bm |
| Length |
|
| Beam | 35 ft 0 in (10.7 m) |
| Depth of hold | 14 ft 0 in (4.3 m) |
| Sail plan | Full-rigged ship |
| Complement | 185 (peacetime) - 280 (wartime) |
| Armament |
|
HMS Dragon was a powerful warship of the English Navy. She was built in 1647 and later became part of the Royal Navy. She was known as a "fourth-rate" ship, meaning she was a medium-sized warship with many guns. Dragon was also one of the first "frigates" built at Chatham Dockyard. In those days, a frigate was a fast ship with a low deck, designed for speed.
Contents
Building and Features of HMS Dragon
HMS Dragon was built at Chatham Dockyard by Henry Goddard. She was launched in 1647. Her main deck for guns was about 120 feet (36.6 meters) long. She was about 28 feet 6 inches (8.7 meters) wide.
When first built, Dragon carried 38 guns during wartime and 32 guns during peacetime. By 1666, she had 42 guns in wartime. These included different types of cannons like culverins (long-range guns) and demi-culverins (medium-range guns). Her crew size changed over time, starting with 150 sailors in 1652 and growing to 160 a year later.
HMS Dragon's Time at Sea
Serving During the English Civil War
Dragon began her service in 1647. She was part of the Parliament's navy during the English Civil War. Her first captain was Anthony Young. She helped recapture a ship called Hart in 1648.
Later, under Captain John Stoakes, she continued to patrol the Irish Sea. After the Civil War ended, she joined the Commonwealth Navy. She fought in several important battles during the First Anglo-Dutch War. These included the Battle of Dungeness in 1652, the Battle of Portland in 1653, and the Battle of the Gabbard in 1653. She also took part in the Battle of Scheveningen in July 1653.
After the war, in 1655, Dragon joined Robert Blake's fleet in the Mediterranean Sea. She returned to English waters in 1656 and served in the English Channel until 1660.
Service After the Monarchy Returned (1660)
After the monarchy was restored in May 1660, Dragon became part of the Royal Navy. In 1665, under Captain John Lloyd, she fought in the Battle of Lowestoft.
She also took part in the Four Days' Battle in 1666, one of the longest naval battles in history. During this battle, she had one sailor killed and six wounded. Later that year, she fought in the St James Day Fight, also known as Orfordness. She was also part of 'Holmes Bonfire', an attack on Dutch ships in the River Vile. The Second Anglo-Dutch War ended in 1667.
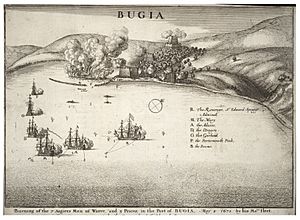
In 1671, Dragon was involved in the Battle of Bugia in the Mediterranean. She also fought against three Algerian ships in 1672. During the Third Anglo-Dutch War, she had a skirmish with two Dutch ships. After many years of service, she returned to England in 1689.
Major Rebuilds of HMS Dragon
HMS Dragon went through two major rebuilds to keep her strong and modern.
First Rebuild in 1689
In 1689, Dragon was rebuilt at Deptford. After this rebuild, she was about 118 feet 11 inches (36.2 meters) long on her gun deck. She was also wider, at 31 feet 9 inches (9.7 meters).
Her gun count changed again. By 1696, she carried 46 guns, including 12-pounder and 8-pounder cannons. Her crew size was set at 220 sailors.
Service After the 1689 Rebuild
After her rebuild, Dragon was sent to serve in Ireland in 1691. She then moved to the English Channel in 1692. In 1693, she sailed to the West Indies.
In 1694, she helped capture a French ship called Diligente. She also escorted a convoy of ships to Turkey in 1695. In 1701, during the War of the Spanish Succession, she fought a French 70-gun ship. Sadly, her captain, Robert Holliman, and 25 other sailors were killed in this battle.
Second Rebuild in 1706
Dragon was rebuilt again in 1706-1707 at Rotherhithe. This made her even larger. Her gun deck was now about 130 feet (39.6 meters) long, and she was 35 feet (10.7 meters) wide.
After this rebuild, she could carry between 46 and 54 guns, depending on whether it was peacetime or wartime. Her crew size also increased to 280 sailors during wartime.
Service After the 1706 Rebuild
In 1707, Dragon was commanded by Captain George Martin. She sailed to the Dutch coast and later to Newfoundland in 1709. In 1710, she went to Nova Scotia and helped capture Annapolis (Port Royal). She returned to England at the end of 1710 and had another refit in 1711.
The Loss of HMS Dragon
Sadly, HMS Dragon was wrecked on March 15, 1712. She ran aground on Les Casquets, which are rocks located west of Alderney island.
Captains of HMS Dragon
- 1647-8 Anthony Young
- 1650-2 John Stoakes
- 1653-5 Edmund Seaman
- 1656-60 Richard Haddock
- 1664 Valentine Pyend?
- 1665 John Lloyd
- 1665-6 Daniel Helling
- 1666 Thomas Roome Coyle
- 1668 Richard May
- 1669-72 Arthur Herbert
- 1672-3 Thomas Chamberlaine
- 1673 David Trotter
- 1674-7 Sir Roger Strickland
- 1682-3 Thomas Hamilton
- 1686-9 Henry Killigrew
- 1691 William Wright
- 1692 - Nov. 1694 William Vickars
- 1695-7 Edward Rigby
- 1701-2 Robert Holliman
- 1702-3 Charles Fotherby (acting)
- 1703-6 Henry Maynard
- 1707-11 George Martin