In vitro fertilisation facts for kids
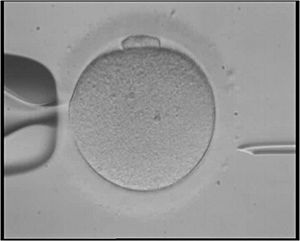
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a special medical procedure. It helps people who have trouble having a baby naturally. With IVF, a sperm cell and an egg cell are joined together outside the body. This happens in a lab, often in a special dish or tube. The term "in vitro" comes from Latin and means "in glass." This refers to the glass containers used in the lab.
Contents
How IVF Was Developed
The idea of IVF came from two doctors in the United Kingdom. Their names were Patrick Steptoe and Robert Edwards. They worked hard to make this new method possible. The very first baby born using IVF was Louise Brown. She was born on July 25, 1978. She was often called the first "test-tube baby."
A few years later, in 1981, the first successful IVF treatment happened in the United States. This led to the birth of Elizabeth Carr. Since then, many thousands of babies have been born thanks to IVF treatment.
Understanding the IVF Process
The IVF process involves several steps. First, doctors carefully collect egg cells from the woman's body. These eggs are then placed in a special liquid in the lab. Next, sperm cells are added to the liquid with the eggs. The goal is for the sperm to fertilise the eggs there.
Once the eggs are fertilised, they become embryos. These tiny new embryos are then gently placed into the mother's uterus. The uterus is also known as the womb. If everything goes well, the embryo will grow and develop normally inside the uterus. This is just like a natural pregnancy.
Why People Use IVF
IVF is a helpful option for many couples. It is often used when a man has a low sperm count. This means there are not enough sperm cells to fertilise an egg naturally. IVF is also used if a woman's fallopian tubes are blocked. Fallopian tubes are tubes that carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. If they are blocked, the egg cannot meet the sperm.
In these situations, IVF can give couples a chance to have a baby. It helps overcome some of the challenges that prevent natural pregnancy.
Images for kids
-
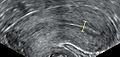
A triple-line endometrium is associated with better IVF outcomes.
See also
 In Spanish: Fecundación in vitro para niños
In Spanish: Fecundación in vitro para niños