Hindu–Arabic numeral system facts for kids
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system is the way we write and use numbers almost everywhere in the world today. This system uses ten basic symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
This number system is very important because it uses a "place value" system. This means the position of a digit in a number changes its value. For example, in the number 25, the '2' means twenty, but in the number 52, the '2' means two. This makes it easy to write and work with very large or very small numbers.
Contents
What Are Hindu-Arabic Numerals?
The Hindu-Arabic numeral system is the most common way to write numbers. It's also known as the decimal system because it's based on ten digits (0 through 9). These digits can be combined to make any number you can imagine.
For example, to write the number "one hundred twenty-three," we use the digits 1, 2, and 3. Their positions tell us their value:
- The '1' is in the hundreds place, meaning 100.
- The '2' is in the tens place, meaning 20.
- The '3' is in the ones place, meaning 3.
Adding these together gives us 100 + 20 + 3 = 123.
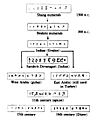
Where Did Hindu-Arabic Numerals Come From?
This amazing number system was first developed by people in India a very long time ago. They created the idea of using a zero and the place value system.
Later, around the 8th and 9th centuries, Arab scholars learned about these numbers from India. They understood how useful the system was. They then helped spread these numbers to the Western world, especially through Europe. That's why it's called the "Hindu-Arabic" system – it combines its Indian origins with the Arab scholars who helped share it globally.
How They Spread Around the World
Before the Hindu-Arabic system, many other number systems were used. For example, the Roman numerals (like I, V, X, L, C, D, M) were common in Europe. However, Roman numerals didn't have a zero and didn't use place value, which made calculations much harder.
When the Hindu-Arabic system arrived in Europe, it slowly replaced the older systems. It made math much simpler and faster. This helped with trade, science, and many other areas of life. Today, it's the standard way to count and calculate all over the world.
Images for kids
-
The first Brahmi numerals, ancestors of Hindu-Arabic numerals, used by Ashoka in his Edicts of Ashoka c. 250 BC
-
The Arabic numeral system first appeared in Europe in the Spanish Codex Vigilanus, year 976.
-
A calculation table, used for arithmetic using Roman numerals
-
Adam Ries, Rechenung auff der linihen und federn, 1522
-
Adam Ries, Rechenung auff der linihen und federn (2nd Ed.), 1525
-
Robert Recorde, The ground of artes, 1543
-
Peter Apian, Kaufmanns Rechnung, 1527
-
Adam Ries, Rechenung auff der linihen und federn (2nd Ed.), 1525
See also
 In Spanish: Numeración indo-arábiga para niños
In Spanish: Numeración indo-arábiga para niños
 | Madam C. J. Walker |
 | Janet Emerson Bashen |
 | Annie Turnbo Malone |
 | Maggie L. Walker |