Jerrold Meinwald facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Jerrold Meinwald
|
|
|---|---|

Meinwald in 2010
|
|
| Born | January 16, 1927 New York City, U.S.
|
| Died | April 23, 2018 (aged 91) Ithaca, New York, U.S.
|
| Alma mater | Harvard University University of Chicago |
| Awards |
|
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Chemistry |
| Institutions | Cornell University |
| Doctoral students | George Wiley |
Jerrold Meinwald (born January 16, 1927 – died April 23, 2018) was an American chemist. He helped start a science field called chemical ecology. He did this with his friend and fellow scientist, Thomas Eisner.
Jerrold was a chemistry professor at Cornell University. He wrote or helped write over 400 science papers. His love for chemistry started when he made fireworks with his friend Michael Cava. They were still in middle school then! Jerrold also loved music. He even learned to play the flute from Marcel Moyse, a very famous flutist.
Contents
Jerrold Meinwald's Career
Jerrold Meinwald was born in 1927 in New York City. He studied chemistry at the University of Chicago. He earned his first degree there in 1948. Later, he went to Harvard University and got his Ph.D. in 1952. After that, he moved to Cornell University. He spent most of his career teaching and researching there.
Studying Chemical Ecology
Since the early 1960s, Jerrold Meinwald worked on how animals use chemicals to communicate. He often worked with Thomas Eisner. They focused a lot on insects and other small creatures. Their work helped create the field of chemical ecology. This science looks at how living things interact using chemicals.
One interesting area they studied was how insects use chemicals from plants. Sometimes, insects use these plant chemicals directly. Other times, they change the plant chemicals to make their own special chemicals.
The Moth and Its Chemical Defenses
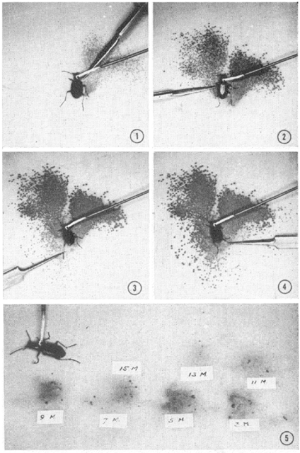
One animal they studied for many years was the moth called Utetheisa ornatrix. This moth collects special chemicals from the plants it eats. These chemicals are called pyrrolizidine alkaloids. The moth uses them to protect itself from animals that might want to eat it. It makes the moth taste bad to predators.
The male moth also uses these chemicals as a pheromone. A pheromone is a chemical signal that animals use to communicate with each other. The male moth passes these chemicals to the female moth when they reproduce. The female then uses them to make her eggs taste bad too. This helps protect the baby moths from predators.
Chemistry Discoveries
Jerrold Meinwald also developed new ways to understand chemical structures. One method he created is called the Meinwald Rearrangement. This is a special chemical reaction. He also spent over 40 years researching NMR spectroscopy. This is a powerful tool that helps chemists figure out the exact structure of molecules.
Jerrold Meinwald passed away in Ithaca on April 23, 2018. He was 91 years old.
Awards and Honors
Jerrold Meinwald received many important awards for his work.
- He won the National Medal of Science in 2012. This is one of the highest science awards in the United States.
- He became a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 1969.
- He was also a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences since 1970.
- In 1987, he joined the American Philosophical Society.
Other important awards he received include:
- Distinguished Leadership Award, American Academy of Arts and Sciences (2016)
- Nakanishi Prize, American Chemical Society (2014)
- Roger Adams Award in Organic Chemistry, American Chemical Society (2005)
- Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement (1990)
See also
 In Spanish: Jerrold Meinwald para niños
In Spanish: Jerrold Meinwald para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |