Kelso Wash facts for kids
Kelso Wash is a special kind of stream in the desert. It's called an ephemeral stream, which means it only flows with water after it rains a lot. You can find Kelso Wash in San Bernardino County, California, in the United States. This stream eventually empties into a dry lakebed called Soda Lake. The small town of Kelso is located to the southeast of this wash.
Contents
Kelso Wash: A Desert Stream
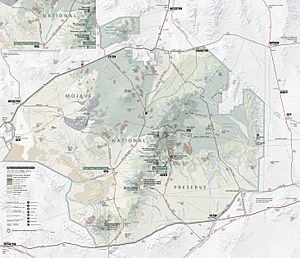
Kelso Wash is an important part of the Mojave National Preserve. This preserve is a large protected area in the desert. The wash begins near a place called Cima. It flows between two mountain ranges: the Kelso Mountains to the west and the Providence Mountains to the east.
Where Kelso Wash Starts and Flows
When Kelso Wash starts, it flows south. It collects water from other smaller washes, like Cedar Wash from the northeast. It also gets water from washes that drain the Marl Mountains to the northwest. A cool volcanic area called the Cima Dome is also nearby.
The area around Cima separates the valley of Kelso Wash from another valley called Ivanpah Valley. As Kelso Wash continues, it turns west. This turn happens just north of the famous Kelso Dunes. Along its path, it picks up more water from other washes.
Joining Other Desert Washes
One of these is Cottonwood Wash, which flows in from the southeast. Cottonwood Wash drains water from the southern Providence Mountains and the Granite Mountains. Another wash that joins Kelso Wash is Budweiser Wash. This one comes from the south and drains areas like the Bristol Mountains, Granite Mountains, and Old Dad Mountains.
After collecting all this water, Kelso Wash travels northwest. It flows between a desert area called Devils Playground to the north and the Bristol Mountains to the south. Finally, it reaches its end at Soda Lake. Kelso Wash is the biggest stream that drains water into the Soda Lake area.
How Kelso Wash Gets Its Water
The Mojave Desert doesn't get much rain. On average, the area around Kelso Wash receives about 100 to 200 millimeters (4 to 8 inches) of rain each year. Even with so little rain, Kelso Wash gets its water from two main sources.
One source is groundwater. This is water that is stored underground, close to the surface. The other source is surface runoff. This is water that flows over the ground after it rains.
The Wash's Changing Path
Over time, sand dunes have often blocked the path of Kelso Wash. When this happened, temporary lakes would form. These lakes would fill up with sediments, like sand and dirt, especially during a period called the early Holocene (thousands of years ago).
The wash has also carved deep into the ground, sometimes as much as 11 meters (about 36 feet) deep. Along its sides, you can see river terraces. These are flat, step-like areas that show where the riverbed used to be at different times. The Union Pacific Railroad tracks run very close to Kelso Wash.
Importance of Kelso Wash
Kelso Wash, along with the Mojave River, helps supply water to the Mojave River sink area. This area is important for desert plants and animals. It also provides water to a small lake called Lake Tuendae.
In 1984, scientists thought that Kelso Wash might be a source of sand for the famous Kelso Dunes. The dunes are huge piles of sand that are constantly shifting with the wind. The sand carried by the wash could have helped build these impressive dunes over many years.