Mojave River facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mojave River |
|
|---|---|

Mojave River at Afton Canyon, March 2010
|
|
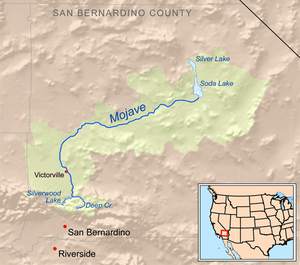
Map of the Mojave River watershed
|
|
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Cities | Hesperia, Apple Valley, Victorville, Barstow |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Confluence of West Fork Mojave River and Deep Creek Mojave River Forks Reservoir, San Bernardino Mountains 2,986 ft (910 m) 34°20′29″N 117°14′14″W / 34.34139°N 117.23722°W |
| River mouth | Soda Lake Baker, Mojave Desert 935 ft (285 m) 35°06′20″N 116°03′53″W / 35.10556°N 116.06472°W |
| Length | 110 mi (180 km) |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 4,580 sq mi (11,900 km2) |
| Tributaries |
|

The Mojave River is a special river in California, United States. It flows through the eastern San Bernardino Mountains and the Mojave Desert. Most of the time, the river flows underground. Its surface channels are usually dry. However, water can be seen at the start of the river and in some rocky areas further down.
Contents
History of the Mojave River
Early People and Explorers
For thousands of years, Native American groups lived along the Mojave River. One group was the Vanyume, a desert branch of the Serrano people. They lived along much of the river, from Barstow to Victorville.
The Mohave people had a trail that followed the river. This trail, later called the Mojave Road, was used for trade. Native Americans could easily find water along this route to the coast.
In 1776, a Spanish priest named Francisco Garcés explored the river. He called it "Arroyo de los Mártires." Later, other Spaniards called it "Río de las Ánimas."
First Americans and New Trails
In 1826, Jedediah Smith was the first American to travel to California by land. He followed the Mohave Indian Trail and called the river the "Inconstant River."
The Old Spanish Trail was a path for pack horses and livestock. It was set up in 1829 between New Mexico and Los Angeles. This trail joined the Mojave River near Soda Lake. It followed the river up to the Cajon Pass, which led into the coastal valleys.
In 1844, John C. Frémont named the river "Mohahve." He named it after the Mohave people, even though they lived far away on the Colorado River. Some early Mormon ranchers called it the Macaby River.
Mormon Road and Mojave Road
From 1847, Mormons created a wagon road from Salt Lake City to Los Angeles. This road followed parts of the Old Spanish Trail. They used the Mojave River's path for a section of their journey.
During the California Gold Rush in 1849, many travelers used this "Southern Route" to California in winter. The Mormon Road became a major trade route between Utah and southern California.
In 1859, the Mohave people's trail was improved and became the Mojave Road. This wagon route followed the Mojave River from near Daggett to Camp Cady. It then continued to Soda Lake and further east to Fort Mojave.
River as a Refuge
From 1863 to 1864, California had a very bad drought. The Mojave River valley became a safe place for cattle. Some smart ranchers saved their animals by using the river's water resources.
River's Journey
The Mojave River starts in the San Bernardino Mountains. The West Fork of the Mojave River flows into Silverwood Lake. This lake sometimes releases water into the river. Further downstream, Deep Creek joins the West Fork. This is where the Mojave River officially begins, just before the Mojave Forks Dam. This dam helps control floods.
After the dam, the Mojave River flows north and east. It mostly flows underground through cities like Hesperia, Victorville, and Barstow.
Near its end, the Mojave River spreads out into a large area called the Mojave River Wash. When there is a lot of water, the river reaches Soda Lake near Baker. In very wet times, it can even reach Silver Lake, which is even further north. For example, in the winter of 2004–2005, the river flowed all the way to Silver Lake. Both Soda and Silver Lakes filled up with several feet of water.
Most of the river's water is hidden underground. The part of the river you can see on the surface is usually dry. But very big floods can happen. For example, during a strong El Niño event in 1993, heavy rains caused the Mojave River to flood. The water flowed over bridges, especially on Bear Valley Road, which separates Victorville and Apple Valley. The water only comes to the surface in places where the rock is solid and water cannot sink in. This happens in areas like the upper and lower narrows near Victorville and in the Afton Canyon area.
Afton Canyon Natural Area
The Afton Canyon Natural Area is a special place within the Mojave Trails National Monument. It is managed by the Bureau of Land Management. You can find it about 37 mi (60 km) northeast of Barstow, along Interstate 15.
Afton Canyon is important because it protects plants and wildlife. It also keeps the beautiful scenery of the Mojave River's riparian area (the area along the river). Efforts are being made to stop damage from off-road vehicles in the riverbed and canyon.
Projects are working to bring the river's health back. They are removing harmful foreign plants, especially a type of plant called Saltcedar. They are also bringing back native California plants. This helps create a healthy home for the local animals and plants.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Río Mojave para niños
In Spanish: Río Mojave para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |




