Lake Manix facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lake Manix |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Location | Mojave Desert |
| Coordinates | 35°00′N 116°35′W / 35.000°N 116.583°W |
| Type | Pluvial lake |
| Etymology | After the nearby Manix railway station |
| Part of | Mojave River system |
| Primary inflows | Mojave River, local washes |
| Primary outflows | Mojave River through Afton Canyon, Baxter Wash or Bristol Lake less likely |
| Surface area | 236 square kilometres (91 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 60 metres (200 ft) |
| Water volume | 1.6–3.2 cubic kilometres (0.38–0.77 cu mi) |
| Surface elevation | 543 metres (1,781 ft) usually |
| Settlements | Yermo, California, Newberry Springs, California, Yermo, California |
Lake Manix was a large ancient lake in the Mojave Desert of California. It was fed by the Mojave River a long time ago. This lake was located in San Bernardino County, California, near the city of Barstow.
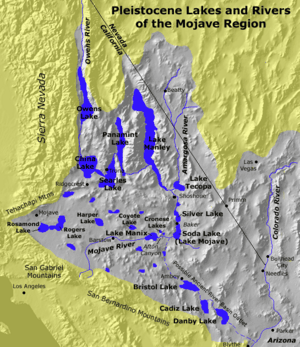
Lake Manix had a unique shape, like a cloverleaf. It spread across four main areas: Coyote, Cady/Manix, Troy, and Afton. The lake covered a huge area of about 236 square kilometers (91 square miles). Its water level often reached about 543 meters (1,781 feet) above sea level.
This ancient lake formed around 500,000 years ago. This happened when the Mojave River changed its path and started flowing into the Manix area. Lake Manix lasted for a very long time, until about 25,000 to 13,800 years ago. It disappeared when a deep channel, called Afton Canyon, formed and drained the lake.
Lake Manix was full of life! It had many different kinds of birds, fish, mammals, and plants. Scientists have also found old tools and other items from early humans in the area. These finds are sometimes called the "Lake Manix Industry."
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name "Lake Manix" was given to this ancient lake in 1913 by a scientist named J. P. Buwalda. He also named the layers of rock and dirt left behind by the lake "Manix Beds."
The name "Manix" comes from a nearby railroad siding (a short railway track) that belonged to the Union Pacific Railroad. This railway stop was located east of Barstow.
Where Was Lake Manix?
Lake Manix was located about 20 to 40 miles (32 to 64 kilometers) east of where Barstow and Daggett are today. It was also close to the small town of Manix, California.
The lake had a special cloverleaf shape. This shape was made up of different basins:
- The Coyote Basin in the northwest.
- The Troy Basin in the south-southeast.
- The Afton Basin in the east-northeast.
Long ago, there was also a Cady Basin. But the Mojave River slowly carved its way through a ridge called Buwalda Ridge. This connected the Cady Basin to the Afton Basin. The total area of the lake was about 236 square kilometers (91 square miles).
Some modern towns, like Yermo, California, Dunn, and Newberry Springs, would have been near the shore of Lake Manix. In some cases, they might have even been underwater!
Lake Levels and Features
The highest level the lake reached was about 543 meters (1,781 feet) above sea level. This stable shoreline suggests that the lake either grew much larger or started to overflow at this point.
You can still see signs of these old shorelines today. They appear as beach bars (underwater sand ridges) and wave-cut cliffs. There was even a lagoon (a shallow body of water) that formed behind one of these beach bars.
Other features found around the lake include alluvial fans (fan-shaped deposits of sediment), deltas (where the river entered the lake), and mudflats. The lake was quite deep, reaching about 60 meters (200 feet) in some places.
Mountains and Earthquakes
Mountains surrounded Lake Manix, including the Cronese Mountains, Cave Mountains, Cady Mountains, Newberry Mountains, Calico Mountains, and Alvord Mountains. These mountains were mostly formed by volcanoes. They also provided sediments that flowed into Lake Manix.
The area around the lake has many faults, which are cracks in the Earth's crust. These faults can cause earthquakes. Scientists have found signs of past earthquakes in the lake's sediments. For example, the 1947 Manix earthquake happened along the Manix fault.
The Mojave River flowed into Lake Manix from the west, likely forming a river delta there. The lake's water eventually drained out through Afton Canyon. This canyon carried the water east towards Soda Lake and Silver Lake, and eventually to Death Valley.
Today, the areas that were once part of Lake Manix are now dry lakebeds, like Coyote Lake and Troy Lake. Modern highways, like Interstate 40 and Interstate 15, now cross the former lake bed.
How Lake Manix Formed and Disappeared
During the ice ages, many lakes filled up in the western United States. This happened because of changes in weather patterns, which brought more rain and snow to these areas. Lake Manix was one of these "pluvial lakes."
The Mojave River was the main source of water for Lake Manix. The lake formed because there was much more rainfall in the San Bernardino Mountains, where the Mojave River begins. Scientists estimate that the amount of water flowing into the area had to increase by about ten times for Lake Manix to form.
Lake Manix held a huge amount of water, possibly as much as 1.6 to 3.2 cubic kilometers (0.38 to 0.77 cubic miles). The water levels in the lake often changed, rising and falling by 5 to 15 meters (16 to 49 feet).
Water Chemistry and Temperature
Scientists have studied tiny fossils, like Ostracods (small crustaceans), found in the lake's sediments. These fossils tell us that Lake Manix was a well-mixed lake, especially in the summer. This means the water temperature was fairly even from top to bottom.
For a long time, the lake was quite cold, with water temperatures not rising above 4 degrees Celsius (39 degrees Fahrenheit). Later, it became warmer again.
Lake Manix and Other Lakes
Lake Manix was not the only lake formed by the Mojave River. Lake Mojave also formed in the Silver Lake and Soda Lake basins. Water from Lake Manix would sometimes spill over into Lake Mojave.
The Mojave River, along with another river called the Amargosa River, also fed Lake Manly in Death Valley. When Lake Manix eventually drained, it sent even more water down to Death Valley.
The amount of water in Lake Manix seemed to increase during both cold and warm periods. This was likely due to changes in storm paths, which brought more moisture to the area. The Mojave River is very sensitive to where storms happen.
Amazing Ancient Life
Lake Manix was home to a wide variety of plants and animals. Scientists have found many fossils in the lake's sediments.
Birds
Many bird skeletons have been found, including:
- Western grebe
- White pelican
- Golden eagles
- Canada geese
- An extinct stork called Ciconia maltha
- Ruddy ducks
- Cranes
- Double-crested cormorants
- And two types of flamingos, Phoenicopterus copei and Phoenicopterus minutus.
These birds are typical of lake environments. Their presence suggests that Lake Manix might have been an important stopover for migrating birds.
Mammals
Fossils of many large mammals have also been discovered around Lake Manix. These include:
- Canis (like wolves or coyotes)
- Felis (like ancient cats)
- Equus (ancient horses)
- Camelops (ancient camels)
- Tanupolama (ancient llamas)
- Ovis (ancient sheep)
- Bison (ancient bison)
- Mammoths
- Nothrotherium (a type of ground sloth)
Other Animals
- Freshwater clams, like Anodonta californiensis, were very common. You can find large deposits of their shells.
- Various types of snails were also present.
- Fish species found include the Mojave tui chub and stickleback.
- The Western pond turtle also lived in the lake.
Tiny Ostracods (small crustaceans with shells) were abundant in the lake. Scientists have found many different species of them. Diatoms (tiny algae) were also present. Even Stromatolites, which are layered structures formed by microbes, grew in the lake.
Plants
The area around Lake Manix had different types of plants than today. There were reedy marshes near the water. Further away, you would find juniper and sage plants, and Pinyon-juniper woodlands in the mountains. Today, the area is mostly covered by creosote bushes.
Climate Then and Now
Today, the climate in the Lake Manix area is very dry and warm. The average temperature in Barstow is about 17.7 degrees Celsius (63.9 degrees Fahrenheit). There's very little rain, only about 125-150 millimeters (5-6 inches) per year. The amount of water that evaporates is much higher than the rainfall.
During the time Lake Manix existed, the climate was much wetter and cooler, allowing the lake to form and thrive.
The Lake's Timeline
The Mojave River's path changed over millions of years. Around 500,000 years ago, it started flowing into the Cady Basin of Lake Manix. At first, the river might have flowed into both Lake Manix and another lake called Harper Lake.
About 190,000 years ago, the Afton Basin became connected to the rest of Lake Manix. This might have happened because of a huge, sudden flood that carved through a ridge.
Scientists have different ideas about exactly when Lake Manix was at its highest levels. Some theories suggest there were three main high water periods during the Pleistocene (Ice Age). Other ideas suggest even more highstands. Recent studies using radiocarbon dating show that the lake had high water levels at many different times, often matching cold and wet periods.
Lake Manix finally drained when Afton Canyon formed. This likely happened around 13,800 years ago. Some scientists believe this draining was very fast, perhaps emptying the lake in just a few hours! This sudden draining would have sent a huge amount of water downstream, possibly helping to fill Lake Mojave even more.
After the initial fast draining, the Afton Canyon continued to get deeper more slowly. The Manix Fault likely helped in forming this canyon, as it created weaker rocks that were easier to erode. Today, the Mojave River usually ends near Victorville, California, and only during very big floods does it reach as far as Soda Lake.
Early Human History
Lake Manix was an important place for early humans living in the area. Evidence suggests that people were present around Lake Manix about 11,500 years ago.
Scientists have found stone tools and other artifacts near the old shorelines of Lake Manix. These tools include hand axes, disks, flakes, and hammerstones. They were grouped together as the "Lake Manix Industry."
Some people thought these tools were made even before the well-known Clovis culture, which would make them very, very old. However, later dating of the "desert varnish" (a dark coating on rocks) on these tools showed that they were made at different times, over a very long period. This means they don't all belong to one single ancient group.