Keyboard layout facts for kids
When you type on a computer or a phone, you use a keyboard layout. This is how the letters, numbers, and symbols are arranged on your keyboard. Different languages and countries often use different layouts to make typing easier. The most common keyboard layout for English is called QWERTY. You've probably seen it on most keyboards! Even though QWERTY is very popular, people have created other layouts, like the Dvorak Simplified Keyboard, hoping they might be faster or more comfortable to use.
Contents
What is a Keyboard Layout?
A keyboard layout is basically the map of your keyboard. It shows where each key is placed and what character it produces when you press it. Think of it like different ways to arrange your school supplies on your desk – some arrangements might be better for different tasks or people.
Why Do We Have Different Layouts?
The main reason for different keyboard layouts is language. Imagine trying to type in Spanish or French if your keyboard only had English letters! Many languages have special characters, accents, or different letter frequencies, so their keyboards are designed to make typing those specific words easier and faster.
QWERTY: The Most Common Layout
The QWERTY layout is named after the first six letters on the top row of keys: Q, W, E, R, T, and Y. This layout was first designed for typewriters in the 1870s. One popular story says it was made to slow typists down so the mechanical arms of the typewriter wouldn't jam. However, another idea is that it helped telegraph operators quickly type common letter combinations. Even though computers don't jam like old typewriters, QWERTY stuck around and became the standard for English speakers.
Dvorak: An Alternative Layout
The Dvorak Simplified Keyboard was created in the 1930s by August Dvorak. He designed it to be more efficient than QWERTY. The Dvorak layout puts the most common letters in English on the "home row" (the middle row where your fingers rest). This means your fingers move less, which can lead to faster typing and less strain. While Dvorak is popular among some typists, it never replaced QWERTY because so many people were already used to the older layout.
Physical vs. Visual Layouts
It's important to know that there are two main types of keyboard layouts:
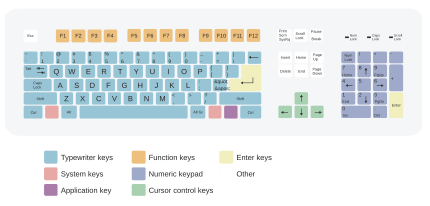
- Physical layout: This is how the keys are actually arranged on the keyboard itself. For example, some keyboards have a big "Enter" key, while others have a smaller one.
- Visual layout: This is what characters are printed on the keycaps. For instance, a keyboard might have a QWERTY physical layout, but the keys could be printed with French (AZERTY) characters. You can also change the visual layout on your computer's settings without changing the physical keyboard.
Common Physical Layouts
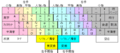
Different countries often use slightly different physical layouts. For example, the ISO standard layout (common in the United Kingdom) has a vertical "Enter" key and a smaller left shift key compared to the ANSI standard layout (common in the United States). The Japanese JIS layout has even more differences, including a smaller space bar to make room for extra keys needed for their writing system.
Keyboard Layouts for Different Languages
Many languages have their own unique keyboard layouts to make typing easier.
- German keyboards often use a QWERTZ layout, where the 'Z' and 'Y' keys are swapped compared to QWERTY.
- French keyboards typically use an AZERTY layout, which changes the position of several letters and symbols.
- Japanese keyboards have special keys to switch between different writing systems, like hiragana, katakana, and kanji.
- Languages with non-Latin scripts like Arabic, Russian, Thai, Sinhala, Tibetan, and Urdu have completely different layouts to match their alphabets. Some of these might also have "phonetic" layouts that try to match the sounds of English letters to their own script.
Special Keyboard Features
Some older or specialized keyboards had very unique layouts and extra keys. For example, the "space-cadet keyboard" from MIT had many "modifier keys" like Control, Meta, Hyper, and Super. These keys, when pressed with other keys, would change what the other keys did, allowing for many more commands. Old mainframe keyboards also had unusual keys like "line feed" or "break."
Today, you can even find virtual keyboards on tablets and phones that let you switch between many different layouts, including historical ones or those for ancient scripts like baybayin.
Images for kids
-
MIT "space-cadet keyboard", an early keyboard with a large number of modifier keys. It was equipped with four keys for bucky bits (Control, Meta, Hyper, and Super); and three shift keys, called "shift", "top", and "front".
-
A comparison of common physical layouts. The ISO-standard physical layout (center left) is common, e.g., in the United Kingdom. Compared with the ANSI layout (top left), the enter key is vertical rather than horizontal. In addition, the left shift key is smaller, to make room for an additional key to its right. The JIS physical layout (bottom right) is the basis for Japanese keyboards. Here it is the right-hand shift key that is smaller. Furthermore, the space bar and backspace key are also smaller, to make room for four additional keys.
-
A screenshot image of the baybayin keyboard on Gboard
-
InScript keyboard layout for Sanskrit
-
Windows Sinhala layout
-
Tibetan keyboard layout
-
Russian phonetic keyboard layout
-
Ukrainian keyboard layout
See also
 In Spanish: Distribución del teclado para niños
In Spanish: Distribución del teclado para niños