Latino-Faliscan languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Latino-Faliscan |
|
|---|---|
| Latinian | |
| Geographic distribution: |
Originally Latium in Italy, later throughout the Roman Empire. |
| Linguistic classification: | Indo-European
|
| Proto-language: | Proto-Latino-Faliscan (Praeneste fibula) |
| Subdivisions: |
Faliscan (extinct)
Lanuvian (extinct)
Praenestinian (extinct)
|
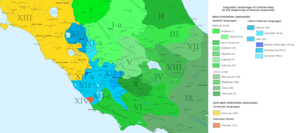 Latino-Faliscan languages and dialects in different shades of blue.
|
|
The Latino-Faliscan languages are a big group of languages. They are part of the larger Italic languages family. These languages were first spoken in what is now Italy. This group is special because it is the only branch of Italic languages that still has living languages today.
The most famous Latino-Faliscan language is Latin. From Latin came the Romance languages, which are still spoken by millions of people around the world. The Roman Empire helped spread Latin across Europe. Over time, Latin changed and split into many different languages. There were also at least three other Latino-Faliscan languages that have now disappeared.
Contents
What are Latino-Faliscan Languages?
Latino-Faliscan languages are a family of languages that are all related. Think of them like a family tree. They all came from an older language that no one speaks anymore. This "parent" language is called Proto-Latino-Faliscan.
These languages were first spoken in a region of central Italy called Latium. This is where the ancient city of Rome was located. The most important language from this group is Latin.
Latin: The Language of Rome
Latin was the language of the ancient Romans. It was spoken in the city of Rome and the areas around it. As the Roman Empire grew, Latin became the main language across a huge part of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
Latin was used for everything. People spoke it in daily life, and it was used for government, laws, and writing. Many important books, poems, and plays were written in Latin. Even today, many scientific words and legal terms come from Latin.
How Latin Spread
The Roman Empire was very powerful. As the Romans conquered new lands, they brought their language with them. Soldiers, traders, and settlers all spoke Latin. Schools taught Latin, and people learned it to get along in the Roman world.
Over hundreds of years, Latin changed in different places. People in different parts of the empire started to speak Latin with their own accents and new words. These changes eventually led to new languages.
The Romance Language Family
The Romance languages are a group of languages that all grew out of Latin. They are called "Romance" because they came from the Romans. These languages include:
There are many other Romance languages too, like Catalan and Galician. Even though they sound different, you can often see similarities between them. This is because they all share Latin as their common ancestor.
Languages That Disappeared
Not all Latino-Faliscan languages survived. Some of them are now extinct. This means no one speaks them anymore. These languages include:
- Faliscan: This language was spoken by the Falisci people, who lived north of Rome. We know about it from old writings found on stones and pottery.
- Lanuvian: This language was spoken in the ancient town of Lanuvium, near Rome.
- Praenestinian: This language was spoken in Praeneste, another ancient town. A famous old pin, called the Praeneste fibula, has one of the earliest known Latin writings on it, but it shows some features of Praenestinian.
These languages died out as Latin became more dominant. People stopped speaking them and switched to Latin instead. Studying these extinct languages helps us understand how languages change over time.
See also
In Spanish: Lenguas latino-faliscas para niños
 | DeHart Hubbard |
 | Wilma Rudolph |
 | Jesse Owens |
 | Jackie Joyner-Kersee |
 | Major Taylor |

