Li Jing (Tang dynasty) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Li Jing
李靖 |
|
|---|---|

Portrait of Li Jing
|
|
| Born | 571 Sanyuan County, Shaanxi
|
| Died | July 2, 649 (aged 77–78) |
| Other names |
|
| Occupation | Military general, military strategist, writer |
| Children |
|
| Parents |
|
| Li Jing | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 李靖 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
Li Jing (born 571, died July 2, 649) was a super-smart military general, a clever planner (strategist), and a writer from ancient China. He lived during the early Tang dynasty and was especially important when Emperor Taizong was in charge.
In 630, Li Jing led a surprise attack with only 3,000 cavalry soldiers. He defeated the powerful Göktürks, who were led by Jieli Khan. This amazing victory helped the Tang Empire take control of the Göktürks. Li Jing and another general, Li Shiji, are known as two of the most important early Tang generals.
Contents
Li Jing's Early Life and Career
Growing Up in the Sui Dynasty
Li Jing was born in 571, when China was under the Northern Zhou dynasty, which came before the Sui dynasty. His family was from the Chang'an area, which was the capital city. His grandfather, Li Chongyi, was a provincial governor. His father, Li Quan, was also a governor.
People said Li Jing was handsome and very ambitious when he was young. He was talented at both writing and military skills. His uncle, Han Qinhu, was a famous general. Han Qinhu was very impressed by Li Jing's abilities. He once told Li Jing, "You are the only person I can talk to about the strategies of Sun Tzu and Wu Qi!"
Starting His Career
Li Jing began his career as a small official in Chang'an county. Later, he worked as a low-level official in the government. He impressed important leaders like Prime Minister Yang Su.
Near the end of Emperor Yang's rule, Li Jing worked in Mayi Commandery. He served under Li Yuan, who was then the Duke of Tang. Li Yuan was in charge of defending the city of Taiyuan against attacks from the Eastern Tujue forces.
Li Jing started to suspect that Li Yuan was planning a rebellion. So, he pretended to commit a crime. He asked to be arrested and sent to Emperor Yang. However, he was first sent to Chang'an. Because the whole Sui state was full of rebellions, he couldn't be sent all the way to Emperor Yang.
A Close Call with Execution
In 617, Li Yuan did rebel and captured Chang'an. He made Emperor Yang's grandson, Yang You, the new emperor. But Li Yuan was the real power behind the throne. Li Yuan knew that Li Jing had tried to report his plans to Emperor Yang. So, he decided to execute Li Jing.
At the execution, Li Jing shouted, "You, duke, rose up to get rid of bad rulers for the people! You are not thinking about what's important. Instead, you are executing a brave man because of a personal grudge!"
Li Yuan was impressed by Li Jing's words. His son, Li Shimin, also spoke up for Li Jing. Li Yuan then released Li Jing. Soon after, Li Shimin asked Li Jing to join his team.
Serving the Tang Dynasty
Helping Emperor Gaozu Expand the Empire
In 618, Emperor Yang was killed in a coup. Li Yuan then became the new emperor, establishing the Tang dynasty. Li Jing continued to serve the new Tang dynasty.
In 619, Li Jing helped in a fight against one of Tang's enemies, Wang Shichong. He was promoted for his success. Later that year, Emperor Gaozu sent him to Kui Prefecture. His mission was to plan a military operation against another big enemy, Xiao Xian.
Li Jing faced bandits in the mountains on his way. He joined forces with another general, Li Yuàn, to defeat them. However, Liang forces blocked his path, and he couldn't reach his destination for a long time. Emperor Gaozu thought Li Jing was intentionally delaying. He secretly ordered Li Jing to be executed. But a local official, Xu Shao, spoke up for Li Jing. He told the emperor how talented Li Jing was, and Emperor Gaozu changed his mind.
Around the same time, a rebel leader named Ran Zhaoze attacked Kui Prefecture. Li Jing reinforced Emperor Gaozu's nephew, Li Xiaogong, with 800 men. They defeated and killed Ran.
Conquering the Liang State
In 621, Li Jing presented 10 strategies to defeat the Liang state. Emperor Gaozu approved his plans. He made Li Jing Li Xiaogong's assistant for the campaign. Li Xiaogong was still young and inexperienced. So, Li Jing was actually in charge of most of the operations.
In late 621, Emperor Gaozu launched a big attack on Xiao Xian's Liang state. The Yangtze River was high and flowing fast. Many officers wanted to wait, but Li Jing suggested using the fast water for a surprise attack on Xiao Xian's capital, Jiangling.
After defeating a Liang general, Li Xiaogong surrounded Jiangling. Li Jing suggested floating captured Liang ships down the Yangtze. This tricked the approaching Liang relief forces into thinking Jiangling had already fallen. Xiao Xian, not knowing help was close, surrendered. Li Jing and Xiao's official, Cen Wenben, convinced Li Xiaogong to prevent looting. Because of this, many Liang provinces soon joined the Tang. Li Xiaogong sent Xiao Xian to Chang'an, where he was executed. For his great work, Li Jing was given the title Duke of Yongkang.
Li Jing then went south to persuade regions in modern Guangdong and Guangxi to join the Tang. He successfully convinced several powerful local leaders to submit to Tang rule.
Defeating Fu Gongshi
In 623, a Tang general named Fu Gongshi rebelled. He declared himself the Emperor of Song. Emperor Gaozu sent Li Xiaogong to attack Fu, with Li Jing as his assistant again.
Li Xiaogong and Li Jing sailed down the Yangtze River. They won many battles against the Song generals. Fu ordered his generals to hold their ground and wear down the Tang forces. But Li Xiaogong, following Li Jing's advice, cut off their supplies. When the Song generals ran out of food, they attacked. Li Xiaogong and Li Jing used a clever trick. They used their weaker forces first to draw the enemy in. Then, they launched a strong attack and defeated them completely.
After this victory, they attacked Fu's capital, Danyang. Fu got scared and ran away, but he was captured and brought back. Emperor Gaozu praised Li Jing, saying, "Li Jing is like a deadly disease for Xiao and Fu! Not even famous generals like Han Xin or Huo Qubing could be better than him!" Li Jing helped a lot in bringing peace to the region after years of fighting.
Facing the Eastern Tujue
In 625, the Eastern Tujue attacked Taiyuan. Li Jing led his troops north to fight them. While other Tang generals were defeated, Li Jing managed to keep his troops safe. In 626, when the Eastern Tujue attacked again, Li Jing tried to cut off their escape route. Soon after, Tang and Eastern Tujue made peace.
Around this time, Li Shimin was in a tough rivalry with his older brother, Li Jiancheng, the Crown Prince. Li Shimin asked Li Jing and Li Shiji for advice. Both refused to get involved in the family struggle, which Li Shimin respected. In 626, Li Shimin killed his brothers at Xuanwu Gate. He then forced Emperor Gaozu to make him Crown Prince and then pass the throne to him. This is how Li Shimin became Emperor Taizong.
Li Jing's Victories Under Emperor Taizong
Li Jing continued to serve in Emperor Taizong's government. He became the minister of justice and later the head of the legislative bureau, a very important position. In 629, he became the minister of war.
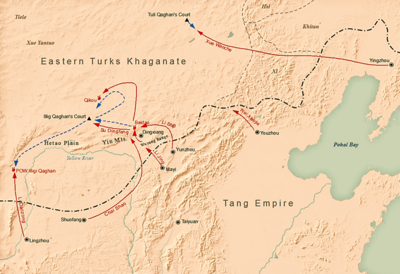
Around 630, the Eastern Tujue were having internal problems. Emperor Taizong decided to attack them. He put Li Jing in overall command of the campaign. Li Jing launched a surprise attack. He captured the important city of Dingxiang. The Eastern Tujue leader, Ashina Duobi, retreated.
Li Jing sent secret messages to convince some of Ashina Duobi's allies to surrender. One of them, Kangsumi, brought Emperor Yang's wife, Empress Xiao, and her grandson, Yang Zhengdao, to surrender to Li Jing. Ashina Duobi sent messengers to Emperor Taizong, offering to surrender. But he was still planning to escape.
Emperor Taizong sent an envoy to Ashina Duobi. He also ordered Li Jing to escort Ashina Duobi. Li Jing understood that Emperor Taizong actually wanted him to attack. So, he joined forces with Li Shiji and launched an attack. They defeated and captured most of Ashina Duobi's remaining forces. Ashina Duobi fled further but was soon captured. All the Eastern Tujue nobles then submitted to Tang.
Emperor Taizong was thrilled with Li Jing's huge victory. He ordered a general pardon and a five-day feast for his people. He also gave Li Jing the higher title of Duke of Dai.
When Li Jing returned to the capital, someone accused him of letting his soldiers loot the Eastern Tujue treasury. Emperor Taizong scolded Li Jing but still rewarded him with more land and silk. Later, Emperor Taizong regretted scolding him. He told Li Jing, "People accused you to hurt you. I understand now. Please don't worry about it." He gave Li Jing even more silk. Later in 630, Li Jing became the head of the executive bureau, another very important government job. People said Li Jing spoke very little when meeting with other leaders. This was seen as a good quality. It also helped him avoid raising Emperor Taizong's suspicions.
Retirement and New Challenges
In 634, Emperor Taizong wanted to send officials to check on different parts of the empire. He wanted them to see if local officials were doing a good job and if people were suffering. Li Jing recommended Wei Zheng for this task. But Emperor Taizong wanted Wei Zheng to stay in the capital. So, Li Jing and 12 other officials were sent out. Li Jing's area was Ji'nei Circuit.
After this trip, Li Jing said he had a foot illness and asked to retire. Emperor Taizong agreed. But he still wanted Li Jing to keep a staff and visit the government offices every few days.
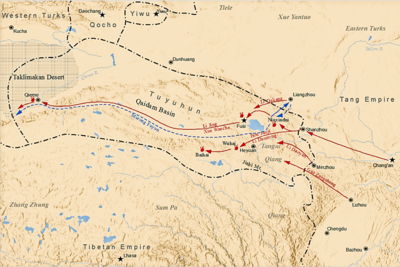
Later in 634, the Tuyuhun attacked Tang. Emperor Taizong wondered who to send as commander. He said, "It would be wonderful to have Li Jing as commander!" When Li Jing heard this, he personally offered to lead the army. Emperor Taizong was very happy. He made Li Jing the commander, with other generals assisting him.
Tang forces won early victories against Tuyuhun. In response, Tuyuhun burned the grass on grazing fields to cut off food for Tang horses. Most Tang generals thought they should retreat. However, General Hou Junji wanted to attack, and Li Jing agreed. They pushed deep into Tuyuhun territory and defeated them greatly. They captured the wives and sons of the Tuyuhun leader, Murong Fuyun. Murong Fuyun's son surrendered, and Murong Fuyun was soon killed. Emperor Taizong made Murong Shun the new leader.
During this campaign, Li Jing once scolded General Gao Zengsheng for arriving late. Gao was unhappy and later accused Li Jing of planning treason. The investigation found no evidence. Gao was accused of making false accusations and was sent away. After this, Li Jing stopped seeing guests and even his relatives very often.
In 637, Emperor Taizong planned to give prefectures to his relatives and great generals as their permanent lands. Li Jing's title was changed to Duke of Wei. But this plan was later canceled, though Li Jing kept his title.
In 640, Li Jing's wife died. Emperor Taizong ordered a special tomb to be built for her. It was shaped like two mountains where Li Jing had won great victories. This was to honor his achievements, just like famous generals from the Han dynasty. In 643, Emperor Taizong honored 24 great contributors to Tang rule with portraits. Li Jing's portrait was one of them.
In 644, Emperor Taizong planned to attack Goguryeo. He asked Li Jing for his opinion. Emperor Taizong said, "You, duke, brought peace to the south, cleared the desert in the north, and settled the Tuyuhun in the west. Only Goguryeo has not surrendered. What do you think?"
Li Jing replied, "Your Majesty, I have, in the past, relied on your power to make my small contributions. I am old and my bones are weak, but if Your Imperial Majesty does not look down on me, I am willing to go despite my sickness."
However, Emperor Taizong saw that Li Jing was ill and decided not to send him. Emperor Taizong later led an attack on Goguryeo himself, which was not very successful. Li Jing died in 649, shortly before Emperor Taizong's own death. He was buried with great honor near Emperor Taizong's tomb.
Li Jing's Writings
Li Jing was one of the best generals and strategists of the Tang dynasty. He was never defeated in his career. He wrote several books about military strategies. Most of his original works are not around today. However, parts of them were mentioned in an old Chinese encyclopedia called the Tongdian.
One famous military book, Duke Li of Wei Answering Emperor Taizong of Tang, is believed to be a conversation between Li Jing and Emperor Taizong. They discuss strategies, policies, and tactics. They even talked about The Art of War and other famous strategy books. This work is said to be by Li Jing, but many modern experts are not sure if he actually wrote it. This is because older books about Li Jing don't mention it.
Li Jing in Stories
Li Jing appears in many Chinese folk tales and novels. Many stories about him were written down in the Taiping Guangji, a collection of stories from the Song dynasty. For example, the novel Romance of Sui and Tang features Li Jing a lot.
The short story Biography of the Dragon-Beard Man is another famous work. It features Li Jing, his wife Zhang Chuchen, and a mysterious man called the "Dragon-Beard Man" who supposedly taught Li Jing military strategies. There is no real proof that these fictional stories are true.
Another novel, Fengshen Yanyi, also has a character named Li Jing. This character seems to borrow some traits from the real Li Jing. However, Fengshen Yanyi is set more than 2,000 years before the historical Li Jing lived. So, it's not the same person.
See Also
- Emperor Taizong's campaign against Tuyuhun