Litmus paper facts for kids
Litmus paper is a special paper used to test if a liquid is an acid or a base (also called an alkali). It's a simple way to find out if a solution is acidic or basic without needing fancy equipment.
Litmus itself is a mix of different dyes that come from tiny plant-like organisms called lichens. This dye is then put onto filter paper to make litmus paper.
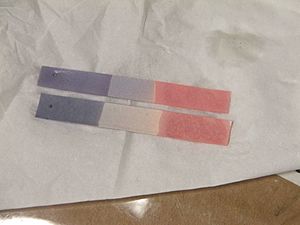
When you use blue litmus paper, it will turn red if you dip it into an acid. If you use red litmus paper, it will turn blue when it touches a base. This color change usually happens when the solution's pH value is between 4.5 and 8.3. You can also use a liquid form of litmus, which works the same way but doesn't need paper.
Contents
History of Litmus
The first known use of litmus was around the year 1300 AD by a Spanish doctor named Arnaldus de Villa Nova. Later, starting in the 1500s, people began to get the blue dye from certain lichens, especially in the Netherlands.
Where Litmus Comes From
Litmus dyes are found in many different types of lichens. Some of the lichens used to make litmus include Roccella tinctoria (from South America), Roccella fuciformis (from Angola and Madagascar), and Parmelia. Today, the main sources for litmus are Roccella montagnei (from Mozambique) and Dendrographa leucophoea (from California).
How Litmus Paper is Used
The main reason people use litmus paper is to check if a liquid is an acid or a base. You can also use wet litmus paper to test for certain gases that dissolve in water and change its acidity or alkalinity. For example, ammonia gas is a base, so it will turn red litmus paper blue.
Remember:
- Blue litmus paper turns red in acidic liquids.
- Red litmus paper turns blue in basic (alkaline) liquids.
- Neutral litmus paper is purple.
The color change happens when the solution's pH is between 4.5 and 8.3 at normal room temperature (about 25 degrees Celsius).
| Litmus (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 4.5 | above pH 8.3 | |
| 4.5 | ⇌ | 8.3 |
Sometimes, other chemical reactions can also change the color of litmus paper. For instance, chlorine gas can turn blue litmus paper white. This happens because the chlorine acts like a bleach and removes the color from the litmus dye. When this happens, the litmus paper isn't acting as a pH indicator anymore because the change is permanent.
How Litmus Works
Red litmus paper contains a weak acid. When it touches a base, the hydrogen parts of the acid react with the base. This reaction changes the structure of the litmus dye, making it appear blue. That's why wet red litmus paper turns blue when it's in a basic solution.
See also
- pH#Indicators
 In Spanish: Tornasol para niños
In Spanish: Tornasol para niños