Littoral (Benin) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Littoral
|
|
|---|---|

Lagoon in Cotonou
|
|
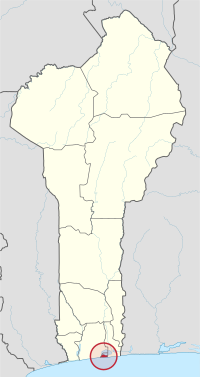
Map highlighting the Littoral Department
|
|
| Country | |
| Capital | Cotonou |
| Area | |
| • Total | 79 km2 (31 sq mi) |
| Population
(2013 census)
|
|
| • Total | 679,012 |
| • Density | 8,600/km2 (22,260/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (WAT) |
Littoral is one of the twelve departments of Benin. It is the smallest department in the country, covering only 79 km2 (31 sq mi). Its capital city is Cotonou, which is also the largest city in Benin. The Littoral department was created in 1999. It was formed when parts of the Atlantique Department were separated to create this new area.
In 2013, a census showed that 679,012 people lived in Littoral. This included 325,872 males and 353,140 females. Everyone in the department lives in urban areas. About 253,892 people in Littoral were part of the workforce. This department has the lowest number of households where people have no formal education.
Exploring Littoral's Nature
The Littoral Department shares its borders with the Ouémé Department and the Atlantique Department. It is located along the coast. This area has many connected lakes and lagoons, along with long coastlines and wide marshy lands.
Fishing, both in freshwater and seawater, is a very important job here. In the 1960s, oil was found offshore. Other important minerals in the region include titanium, iron ore, ilmenite, and chromite.
Benin has different rainy seasons. The southern parts of the country, where Littoral is, usually get rain from March to July and again from September to November. The northern parts have one rainy season from May to September. On average, Benin gets about 1,200 mm (47 in) of rain each year. However, the Littoral Department receives less rainfall than this average.
The land in Littoral is mostly flat and sandy coastal plains near the Atlantic Ocean. There are also many marshes, lagoons, and lakes. The highest point in the coastal plains is about 20 m (66 ft) above sea level. This is much lower than the country's average elevation of 200 m (660 ft).
People of Littoral
| Religious census | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | Percent(%) | |||
| Muslim | 16.9% | |||
| Methodist | 3.7% | |||
| Vodoun | 1.6% | |||
| Catholic | 51.2% | |||
| Celestial | 5.7% | |||
| Other Christian | 12.2% | |||
| Other Traditional | 0.3% | |||
| Other | 2.7% | |||
| Other Protestant | 2.1% | |||
According to Benin's 2013 census, the Littoral Department had a total population of 679,012 people. Out of these, 325,872 were males and 353,140 were females. This means that about 52% of the population were women. Everyone in the department lives in cities or towns.
About 28% of the women were of childbearing age (15 to 49 years old). There were 57,516 foreign people living in the department. This made up about 8.5% of the total population. About 40.7% of foreigners aged 15–64 years were working. Women made up about 48.9% of the foreign population.
The department had 166,433 households, and the average household size was 4.1 people. The population grew by 0.2% between the censuses.
For women, the average age for getting married for the first time was 23.4 years. The average age for having their first child was 29 years. The average number of children a woman would have in her lifetime was 3.7. On average, there was 1.1 family per house and 1.7 people per room.
The total number of people working in the department was 253,892. About 46% of these workers were women. Only 21.1% of households had no one with formal education. A high number, 88.5%, of households had children attending school.
How Littoral is Governed
The Littoral department was created in 1999. It was separated from the Atlantique Department. Cotonou was made its capital. Littoral is the smallest department in Benin.
Littoral has only one main area, which is the city of Cotonou. Cotonou is the largest city in Benin and is its economic capital. Cotonou is further divided into 13 smaller areas called arrondissements. These arrondissements are then divided into 165 neighborhoods.
Benin originally had six administrative regions, which have now been split into 12. Each of the government's local offices manages two administrative regions. A law passed in 1999 changed the lowest level of local government, called sous-prefectures, into local governments. Cities and local councils have elected representatives. These representatives manage the administration of their regions. The most recent elections for these local councils were held in June 2015.
See also
 In Spanish: Departamento Litoral (Benín) para niños
In Spanish: Departamento Litoral (Benín) para niños
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |