Lobotomy facts for kids
Lobotomy is a type of brain surgery. It is also known as leucotomy. A Portuguese doctor named António Egas Moniz invented it in 1935. He even won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1949 for his work on it.
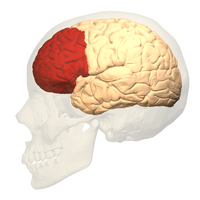
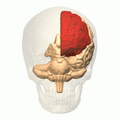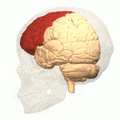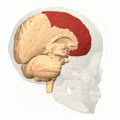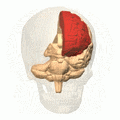
The surgery cut connections in the front part of the brain. This area is called the pre-frontal cortex. It is part of the frontal lobes. This part of the brain is important for thinking and personality.
Moniz first used this method for certain mental illnesses. At that time, there were no other treatments. He first used it on patients with obsessive behavior. These patients would repeat actions over and over. It was also used to treat other mental illnesses. These included schizophrenia and clinical depression.
How Lobotomies Affected People
The main problem with lobotomies was that they changed a person's personality forever. They also changed their behavior. Sometimes, the results seemed good. Patients who had been violent became calm.
But later studies showed some people had serious personality damage. They often had very little 'drive' or motivation. This meant they did not want to do much.
Today, doctors use antipsychotic drugs to treat these problems. An example is chlorpromazine. Lobotomies are now very rarely done.
Why Lobotomies Were Used
Many people wonder why such a big surgery became so popular. Doctors called psychiatrists wanted to help many patients. Thousands of people were in mental hospitals in the 1900s. There were not many other ways to help them.
Also, these patients often had little power. They could not easily refuse the treatments. Doctors in these hospitals sometimes tried new and risky methods.
Images for kids
-
Brain animation: left frontal lobe highlighted in red. Moniz targeted the frontal lobes in the leucotomy procedure he first conceived in 1933.
See also
 In Spanish: Lobotomía cerebral para niños
In Spanish: Lobotomía cerebral para niños