Mach number facts for kids
The Mach number is a special number that helps us understand how fast something is moving. It compares the speed of an object to the speed of sound in the air around it. Think of it like a percentage, but for speed! For example, if something is moving at half the speed of sound, its Mach number is 0.5. If it's moving at the exact speed of sound, it's Mach 1.
We can write it as a simple math formula: 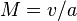 Here, v is the speed of the object, and a is the speed of sound.
Here, v is the speed of the object, and a is the speed of sound.
The Mach number is named after an Austrian scientist named Ernst Mach. When we talk about speed using Mach numbers, we always say the number after the word "Mach."
Contents
What is the Mach Number?
The Mach number tells us how many times faster or slower an object is compared to the speed of sound. The speed of sound changes depending on things like temperature and how high up you are. For example, sound travels faster in warmer air and slower in colder air. It also travels slower at higher altitudes where the air is thinner.
This number is super important for designing and flying fast airplanes and rockets. It helps engineers understand how air flows around these objects at very high speeds.
Understanding the Speed of Sound
Sound travels as waves through the air. Imagine dropping a pebble in a pond; ripples spread out. Sound waves are similar, but they travel through air. The speed of sound is how fast these waves move. On a typical day at sea level, the speed of sound is about 1,235 kilometers per hour (767 miles per hour).
When an object moves, it pushes the air in front of it. If it moves slower than sound, the air has time to get out of the way. But if it moves at or above the speed of sound, the air can't move fast enough. This creates special effects, like shock waves.
Different Mach Speeds
Scientists and engineers use the Mach number to describe different speed ranges. Each range has unique challenges and effects on aircraft.
Subsonic (Below Mach 1)
When an object travels slower than the speed of sound, it is called subsonic. Most regular airplanes, cars, and even birds fly at subsonic speeds. At these speeds, the air flows smoothly around the object. There are no sudden changes in air pressure.
For example, a commercial passenger jet usually flies at about Mach 0.8. This means it's traveling at 80% of the speed of sound.
Transonic (Around Mach 1)
Transonic speeds are very interesting. This is when an object is moving right around the speed of sound (Mach 0.8 to Mach 1.2). At these speeds, some parts of the air flowing over the object might be moving faster than sound, while other parts are still moving slower.
This mix of speeds can cause problems like increased drag and vibrations. It's a tricky speed range for aircraft designers. The vapor cone you see in the picture happens at transonic speeds.
Supersonic (Above Mach 1)
When an object moves faster than the speed of sound, it is called supersonic. Fighter jets and some special passenger planes like the Concorde could fly at supersonic speeds. When an object breaks the sound barrier (goes from transonic to supersonic), it creates a loud sonic boom.
A sonic boom is a powerful shock wave that sounds like an explosion. It happens because the object is pushing through the air faster than the sound waves can get out of the way. These shock waves spread out behind the object.
Hypersonic (Very High Mach)
Hypersonic speeds are extremely fast, usually Mach 5 or higher. This is five times the speed of sound or more! Rockets entering or leaving Earth's atmosphere and some experimental aircraft can reach these speeds.
At hypersonic speeds, the air around the object gets incredibly hot due to friction. This heat can be so intense that it makes the air glow. Special materials are needed to protect hypersonic vehicles from burning up.
Who Was Ernst Mach?
Ernst Mach (1838–1916) was an important physicist and philosopher from Austria. He studied how objects move through fluids like air and water. He was especially interested in what happens when objects move very fast, close to or above the speed of sound.
Mach's work helped us understand shock waves and how they form. His research was so important that the "Mach number" was named in his honor. His ideas laid the groundwork for modern aerodynamics, which is the study of how air interacts with moving objects.
Why is the Mach Number Important?
The Mach number is crucial for many reasons, especially in aviation and space travel.
- Aircraft Design: Engineers use Mach numbers to design planes that can fly efficiently at different speeds. They need to know how air will behave around the wings and body of the aircraft.
- Flight Safety: Pilots need to know their Mach number to avoid dangerous conditions, especially when approaching or exceeding the speed of sound.
- Space Exploration: Rockets and spacecraft travel at very high Mach numbers. Understanding these speeds helps engineers design vehicles that can withstand extreme forces and temperatures during launch and re-entry into Earth's atmosphere.
- Military Applications: Many military aircraft, like fighter jets, are designed to fly at supersonic speeds for tactical advantages.
The Mach number is a simple yet powerful tool that helps us explore the limits of speed and design amazing machines that can travel faster than sound.
See also
 In Spanish: Número Mach para niños
In Spanish: Número Mach para niños


