Mercury, Nevada facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Mercury
|
|
|---|---|
|
Village
|
|

Photo courtesy of the National Nuclear Security Administration Nevada Site Office
|
|
| Country | United States |
| State | Nevada |
| County | Nye |
| Founded | 1950 |
| Named for | Mercury |
| Elevation | 3,789 ft (1,155 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (PST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| ZIP codes |
89023
|
| GNIS feature ID | 845560 |
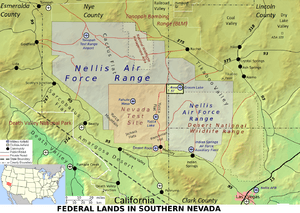
Mercury is a special village in Nye County, Nevada, USA. It is not open to the public. This village is located inside the Nevada National Security Site. It was built by a government group called the Atomic Energy Commission. Mercury's purpose was to house and support the people who worked at the test site. It is about 65 miles northwest of Las Vegas. The village was named after old mercury mines in the area.
History of Mercury Village
The village started in 1950 as "Base Camp Mercury." It was like a military camp. Its goal was to provide basic places for workers at the Nevada Test Site. As more tests happened, more people were needed. So, in 1951, a big project began to build proper homes and offices.
This project cost $6.7 million. The new buildings made the camp look more like a civilian village. In the mid-1950s, it got a full post office. That's when Base Camp Mercury officially became "Mercury, Nevada."
In 1957, the US Navy used Mercury as a base. They launched nine rockets from there. These rockets went into the air to measure things like nuclear radiation. This helped them collect important information about the atmosphere.
By the early 1960s, Mercury's population grew to over 10,000 people. More construction made the village even better. A school was built for children living there. Many fun places were added too. These included a movie theater, a bowling alley, and a swimming pool. There was also a health clinic, a library, and places to stay like the Atomic Motel. A chapel, a gas station, and a bus station were also built. In 1962, the Desert Rock Airport was added. This was for a visit from President John F. Kennedy on December 8.
Mercury thrived until 1992. That's when most nuclear testing stopped at the Nevada Test Site. This happened because the United States agreed to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty. After that, the village's population quickly became much smaller. Many buildings were left empty. Today, a small group of scientists and military staff still work in Mercury. They do limited testing and research. Most of the old facilities are closed. However, there are still dining places, a bar, and a gym. The exact number of people living there now changes often. The last known count was about 500 people.
Geography and Climate
Mercury is located in a desert area. This means it has a very dry climate.
Mercury's Climate
Mercury has a cold desert climate. This type of climate is known as "BWk" on climate maps. It means the area is very dry and can have cold winters. The hottest temperature ever recorded in Mercury was 114°F (45.6°C) on July 11, 2021. The coldest temperature recorded was 6°F (-14.4°C) on December 22, 1990.
| Climate data for Mercury, Nevada (Desert Rock Airport), 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1978–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 77 (25) |
83 (28) |
87 (31) |
96 (36) |
106 (41) |
113 (45) |
114 (46) |
112 (44) |
110 (43) |
103 (39) |
85 (29) |
74 (23) |
114 (46) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 68.0 (20.0) |
71.5 (21.9) |
80.0 (26.7) |
88.7 (31.5) |
96.9 (36.1) |
105.3 (40.7) |
108.9 (42.7) |
106.1 (41.2) |
100.8 (38.2) |
90.7 (32.6) |
77.8 (25.4) |
67.3 (19.6) |
109.8 (43.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 56.6 (13.7) |
59.9 (15.5) |
67.4 (19.7) |
74.2 (23.4) |
83.8 (28.8) |
94.7 (34.8) |
100.7 (38.2) |
98.8 (37.1) |
91.1 (32.8) |
78.1 (25.6) |
64.6 (18.1) |
55.0 (12.8) |
77.1 (25.0) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 45.0 (7.2) |
47.9 (8.8) |
54.1 (12.3) |
60.3 (15.7) |
69.5 (20.8) |
79.6 (26.4) |
86.0 (30.0) |
84.3 (29.1) |
76.3 (24.6) |
64.0 (17.8) |
51.6 (10.9) |
43.6 (6.4) |
63.5 (17.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 33.4 (0.8) |
35.8 (2.1) |
40.9 (4.9) |
46.5 (8.1) |
55.2 (12.9) |
64.4 (18.0) |
71.3 (21.8) |
69.7 (20.9) |
61.5 (16.4) |
49.9 (9.9) |
38.5 (3.6) |
32.2 (0.1) |
49.9 (10.0) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 23.0 (−5.0) |
26.0 (−3.3) |
30.0 (−1.1) |
35.1 (1.7) |
42.7 (5.9) |
52.3 (11.3) |
62.4 (16.9) |
60.1 (15.6) |
50.6 (10.3) |
38.4 (3.6) |
26.8 (−2.9) |
22.3 (−5.4) |
20.0 (−6.7) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 13 (−11) |
11 (−12) |
23 (−5) |
23 (−5) |
33 (1) |
40 (4) |
51 (11) |
52 (11) |
39 (4) |
28 (−2) |
19 (−7) |
6 (−14) |
6 (−14) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.68 (17) |
0.94 (24) |
0.58 (15) |
0.36 (9.1) |
0.18 (4.6) |
0.12 (3.0) |
0.32 (8.1) |
0.39 (9.9) |
0.38 (9.7) |
0.37 (9.4) |
0.27 (6.9) |
0.63 (16) |
5.22 (132.7) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 0.3 (0.76) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
1.0 (2.5) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 4.2 | 4.5 | 3.6 | 2.6 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 3.2 | 30.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| Source 1: NOAA | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: National Weather Service | |||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Mercury (Nevada) para niños
In Spanish: Mercury (Nevada) para niños