Monetarism facts for kids
Monetarism is an idea about how a government should manage a country's economy. It's based on the belief that controlling the amount of money in circulation is the best way to keep the economy healthy.
This idea suggests that if there's too much money, prices go up (this is called inflation). If there's too little money, businesses might struggle, and people could lose jobs.
Contents
What is Monetarism?
Monetarism is an economic theory that focuses on the supply of money. It says that the amount of money available in an economy is the main thing that affects prices and how the economy grows.
How Does Money Supply Work?
The "money supply" is all the money that people and businesses have. This includes cash, money in bank accounts, and other easy-to-access funds.
- When the money supply grows too fast, there's more money chasing the same amount of goods. This can make prices go up, leading to inflation.
- When the money supply grows too slowly, there might not be enough money for people to buy things. This can slow down the economy and lead to job losses.
Who Was Milton Friedman?
The most famous person connected to monetarism was an economist named Milton Friedman. He was an American economist who lived from 1912 to 2006.
- Friedman believed that governments should focus on keeping the money supply steady.
- He thought that if the government tried to control the economy too much, it could actually make things worse.
- His ideas became very important in the 1970s and 1980s, influencing how many countries managed their economies.
Why is Money Supply Important?
Controlling the money supply is a big job for a country's central bank (like the Federal Reserve in the United States). They try to find the right balance.
Fighting Inflation
Inflation means that your money buys less than it used to. For example, if a candy bar cost $1 last year and $1.10 this year, that's inflation.
- Monetarists believe that too much money in the economy causes inflation.
- To fight inflation, a central bank might try to slow down how fast the money supply grows. This can be done by making it more expensive for banks to borrow money.
Supporting Economic Growth
A healthy economy means that businesses are doing well, and people have jobs.
- Monetarism suggests that a stable money supply helps businesses plan for the future.
- When the money supply is predictable, it's easier for companies to invest and create new jobs.
Monetarism in History
Monetarism became very popular in the 1970s and 1980s. Before that, many governments tried to control the economy in other ways.
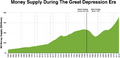
The Great Depression
Milton Friedman and other monetarists studied events like the Great Depression in the 1930s.
- They argued that a big reason for the Depression was a sharp drop in the money supply.
- This drop made it very hard for businesses to operate and for people to spend money, making the economic problems much worse.
Government Policies
Many governments, including those in the United States and the United Kingdom, used monetarist ideas in their policies.
- They focused on controlling interest rates and the amount of money banks could lend.
- The goal was to keep prices stable and help the economy grow steadily.
Images for kids
-
Money supply decreased significantly between Black Tuesday and the Bank Holiday in March 1933 in the wake of massive bank runs across the United States.
See also
 In Spanish: Monetarismo para niños
In Spanish: Monetarismo para niños