Opportunity (rover) facts for kids

An artist's portrayal of Opportunity on the surface of Mars.
|
|
| Mission type | Mars rover |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA |
| Mission duration | Planned: 90 sols (92.5 Earth days) Actual: 5,352 sols (8 Mars years), 5,498 days (15 Earth years) |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | Rover |
| Launch mass | Total: 1,063 kg
|
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | July 8, 2003, 03:18 UTC |
| Rocket | Delta II 7925H-9.5 |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral SLC-17B |
| Contractor | Boeing |
| End of mission | |
| Declared | February 13, 2019 |
| Last contact | June 10, 2018 |
| Mars rover | |
| Landing date | January 25, 2004, 05:05 UTC SCET MSD 46236 14:35 AMT |
| Landing site | 1°56′46″S 354°28′24″E / 1.9462°S 354.4734°E Eagle, Meridiani Planum |
| Distance covered | 45.16 km (28.06 mi) |
 The launch patch for Opportunity, featuring Duck Dodgers (Daffy Duck) NASA Mars rovers
|
|
Opportunity, also known as MER-B or Oppy, was a robot rover that explored the planet Mars. It was active from 2004 until mid-2018. Opportunity was part of NASA's Mars Exploration Rover program. It launched on July 7, 2003.
Oppy landed on Mars on January 25, 2004, in a flat area called Meridiani Planum. This was three weeks after its twin rover, Spirit, landed on the other side of Mars. Both rovers were designed to work for only 90 Martian days (about 92.5 Earth days). However, Opportunity kept working for over 15 Earth years!
Opportunity stayed active for so long by recharging its batteries using solar power. It would also "hibernate" during big dust storms to save energy. This careful operation allowed Opportunity to work 57 times longer than planned. By June 10, 2018, when it last contacted NASA, the rover had traveled over 45 kilometers (28 miles).
Some of Opportunity's main achievements include finding meteorites, like Heat Shield Rock. It also spent over two years exploring Victoria crater. In 2011, it reached Endeavour crater, which was like a "second landing site." The Opportunity mission is seen as one of NASA's most successful space projects.
In June 2018, a huge dust storm covered Mars. Opportunity stopped communicating on June 10 and went into a sleep mode to save power. NASA hoped it would wake up when the storm cleared. But it never did. This likely happened because dust covered its solar panels, or it had a major problem. NASA tried to contact the rover over 1,000 times. On February 13, 2019, NASA announced that the Opportunity mission was officially over.
Contents
Exploring Mars: The Mission of Opportunity
The Opportunity and Spirit rovers were part of the Mars Exploration Rover program. This program was part of NASA's bigger plan to explore Mars. The main goals were to find out if life could exist on Mars. Scientists wanted to see if water could be found there. They also wanted to learn about Mars' climate and geology. Finally, they aimed to prepare for future human missions to Mars.
The Mars Exploration Rovers were designed to travel across the Martian surface. They would study rocks and soil to see if water ever existed on Mars. They also looked for different types of minerals. This information helped confirm data gathered by other spacecraft, like the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Spirit and Opportunity were launched about a month apart in 2003. Both reached Mars in January 2004. Even though they were built for only 90 Martian days, they both lasted much longer. Spirit worked for 20 times its expected life. Its mission ended in 2011 after it got stuck in soft sand. Opportunity worked for an amazing 55 times its planned life! It operated for over 15 years from landing until its mission ended.
Opportunity's Discoveries on Mars
When Opportunity landed, it was by chance in a small crater on a flat plain. It successfully studied soil and rock samples. It also took amazing panoramic photos of its landing site. Its findings helped scientists guess that hematite was present. This also suggested that water existed on Mars in the past.
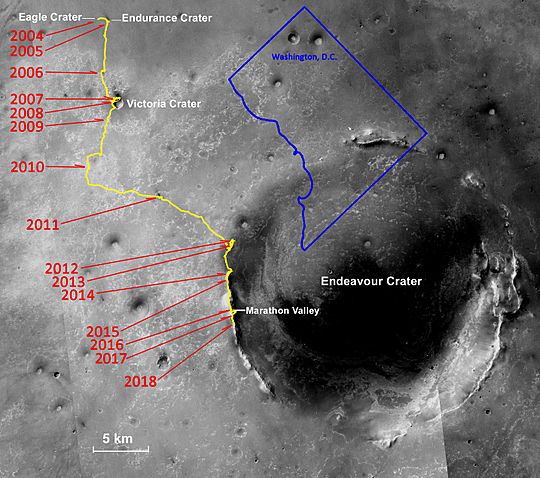
After this, Opportunity traveled across Mars to explore another crater called Endurance crater. It studied this crater from June to December 2004. Later, Opportunity found its own heat shield impact site. There, it discovered an intact meteorite on the surface of Mars. This meteorite is now known as Heat Shield Rock.
In 2005, Opportunity got stuck in a sand dune. Several of its wheels were buried. For six weeks, scientists on Earth practiced how to get the rover out. They used models to make sure they didn't damage it. Slowly, moving just a few centimeters at a time, they freed the rover. It then continued its journey.
Opportunity then headed south to Erebus crater. This was a large, shallow crater on its way to Victoria crater. It explored Erebus between October 2005 and March 2006. During this time, it had some small problems with its robotic arm.
In September 2006, Opportunity reached Victoria crater. It explored the rim of the crater. In 2007, it entered the crater for a detailed study. In August 2008, Opportunity left Victoria crater for Endeavour crater. It finally reached Endeavour on August 9, 2011.
At Endeavour crater, the rover moved around a feature called Cape York. Another spacecraft, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, had found certain minerals there. Opportunity used its tools to check these findings on the ground. It studied this area until summer 2013. In May 2013, the rover started heading south to a hill named Solander Point.
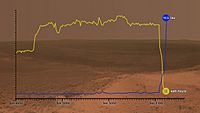
By June 10, 2018, Opportunity had driven a total of 45.16 kilometers (28.06 miles). This was a record for a rover on another planet!
The End of Opportunity's Journey
In early June 2018, a huge dust storm grew on Mars. Within days, the rover's solar panels could not make enough power to communicate. The last contact was on June 10, 2018. NASA hoped to talk to the rover again after the storm. But Opportunity stayed silent, even after the storm ended in October. This suggested a major problem or that dust had completely covered its solar panels. The team hoped strong winds might clear the dust, as had happened before.
On February 12, 2019, past and present mission team members gathered at NASA's Space Flight Operations Facility. They watched as the final commands were sent to Opportunity. These commands were sent through a huge antenna in California. After 25 minutes, the attempts to contact the rover were handed over to a station in Australia.
NASA sent over 1,000 recovery commands to the rover since June 2018. But Opportunity never responded. On February 13, 2019, NASA officials held a press conference. They officially declared the Opportunity mission complete. As NASA ended their attempts, the last data sent to the rover was the song "I'll Be Seeing You" by Billie Holiday. The resources used for Opportunity were then moved to support other Mars rovers, Curiosity and Perseverance.
The very last message from Opportunity came on June 10, 2018. It showed that its solar panels were making very little power. It also showed the highest amount of dust in the Martian atmosphere ever measured.
Images for kids
-
Opportunity rover's "off-world" driving distance record, compared to other rovers. Dashed grey vertical bar shows the Marathon distance.
See also
 In Spanish: Opportunity para niños
In Spanish: Opportunity para niños