Organic light-emitting diode facts for kids
An Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) is a special kind of light-emitting diode (LED). It creates light using a super thin layer of organic compounds. Think of it as a tiny light bulb made from natural materials!
OLED technology is often used for thin display screens in things like notebooks and smartphones. Because of how they are built, OLED displays can even bend and be flexible. This means they could be used in many cool ways, like in clothing or roll-up screens!
Contents
What Makes OLEDs Special?
OLEDs have some great features that make them different from other display technologies, like LCDs.
OLED Advantages
- Better Colors and Brightness: OLEDs can show more colors and different levels of brightness than regular LEDs.
- Great Viewing Angles: Their colors don't change or look weird when you look at the screen from the side.
- Cheaper to Make: It can be less expensive to produce OLED screens.
- No Backlight Needed: Most LCDs need a backlight (like an LED or CCFL) to shine light through them. OLEDs make their own light, so they don't need a backlight.
- Less Power: Because they don't need a backlight and don't use many filters, OLEDs often use less power than LCDs.
- Super Fast: OLEDs can turn on and off much faster than LCDs. This makes them great for fast-moving videos and games.
OLED Disadvantages
- Shorter Lifespan: This is the biggest challenge for OLEDs. Most OLED displays today last about 5,000 hours of use. Regular LEDs, however, can last around 60,000 hours. Scientists are working hard to make them last longer. In 2007, some experiments created an OLED that worked for an amazing 198,000 hours!
- Sensitive to Water: The organic materials inside OLEDs can be easily damaged by water.
- Patents: Companies like Eastman Kodak own patents on OLED technology. This means other companies have to pay a fee to use OLEDs in their products.
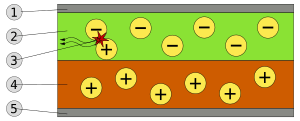
How OLEDs Work
An OLED is made of several very thin layers. Let's look at the main parts:
- Substrate: This is the base material that all the other layers are built on.
- Emissive Layer: This is the special layer where the light is actually created.
- Conductive Layer: This layer helps electricity move through the OLED.
- Anode: This is one of the electrical connections, like a positive (+) terminal.
- Cathode: This is the other electrical connection, like a negative (−) terminal.
The emissive and conductive layers are made from special organic molecules that can carry electricity. The anode and cathode connect the OLED to a power source, like a battery.
Making Light
When electricity flows into an OLED, something cool happens! 1. The emissive layer gets a negative electrical charge. 2. The conductive layer gets a positive electrical charge. 3. Because of these opposite charges, tiny particles called electrons move from the positive conductive layer towards the negative emissive layer. 4. When these electrons move and change their energy levels, they release energy in the form of radiation. This radiation is what we see as visible light!
Just like all diodes, OLEDs only work if electricity flows through them in the correct direction. The anode needs to have a higher electrical potential (more volts, or be more positive) than the cathode for the OLED to light up.
Images for kids
-
OLED lighting in a shopping mall in Aachen, Germany
See also
 In Spanish: Diodo orgánico de emisión de luz para niños
In Spanish: Diodo orgánico de emisión de luz para niños
 | Stephanie Wilson |
 | Charles Bolden |
 | Ronald McNair |
 | Frederick D. Gregory |