Orinoco Delta facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Orinoco Delta |
|
|---|---|
| Delta del Orinoco | |

Orinoco Delta's sunset
|
|
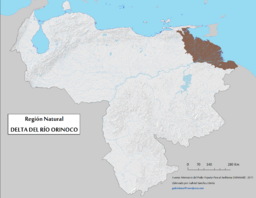
Geographic map of the Orinoco Delta natural region.
|
|
| Location | Delta Amacuro, Monagas & Sucre, Venezuela |
| Coordinates | 9°N 61°W / 9°N 61°W |
| Part of | Orinoco Basin |
| Surface area | 43,646 km2 (16,852 sq mi) |
The Orinoco Delta is a huge river delta in eastern Venezuela. It is formed by the Orinoco River as it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. This special area is full of winding waterways and rich nature.
Contents
Where is the Orinoco Delta?
The Orinoco Delta is one of the eight main natural regions of Venezuela. It covers almost all of Delta Amacuro State. It also includes small parts of Monagas State and Sucre State. This region holds all the places where the Orinoco River meets the sea.
The delta has two main parts. The first part is in the north. It is found between a river branch called Caño Manamo and the left side of Caño Araguao. Most villages are here, including Tucupita, the state capital. The second part is between the right side of Caño Araguao and a larger river branch called Río Grande.
The Warao people, who are an indigenous group, have lived in this region for a very long time. They have a deep connection to the delta's rivers and forests.
How the Orinoco Delta Works
The Orinoco Delta looks like a giant fan. It is formed when the Orinoco River splits into many smaller rivers. These smaller rivers are called caños. They twist and turn through the delta on their way to the ocean. The biggest caño is the Rio Grande. It flows south-southeast through the lower part of the delta. The second most important caño is Caño Manamo. It runs north along the western edge of the delta.
This whole delta area is about 43,646 square kilometers (16,852 square miles). It is special because it doesn't have a central point or many large lakes. It is very open to the ocean, much like the delta of the Niger River in Africa.
Every day, ocean tides bring seawater up the caños. This can cause a strong wave called a "macareo" or pororoca. This wave can even make the water flow backward for a short time, especially on the surface.
Nature and Wildlife of the Delta
The Orinoco Delta is home to amazing plant life. Most of the plants are part of the Orinoco Delta swamp forests ecoregion. This means there are many trees and plants that love wet, swampy conditions.
Along the coast and the edges of the rivers, you can find thick areas of Amazon–Orinoco–Southern Caribbean mangroves. These are special trees that grow in salty water. They are part of the Guianan mangroves ecoregion.
Towards the west, closer to the coast, there are also parts of the Orinoco wetlands ecoregion. These are areas of land that are always wet or flooded.
The delta has huge areas of permanent wetlands. It also has forests that get flooded with fresh water during certain seasons. The edges of the delta's rivers are lined with mangrove trees. These trees are very important for the local ecosystem.
See also
 In Spanish: Delta del Orinoco para niños
In Spanish: Delta del Orinoco para niños

