Parliament of Egypt facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Parliament of Egypt |
|
|---|---|
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | • Senate • House of Representatives |
| Structure | |
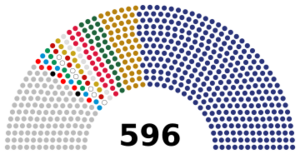
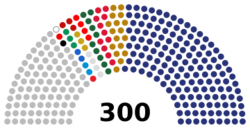
| Seats | 596 Members of the Egyptian House of Representatives (First Chamber of Parliament) 300 Members of the Egyptian Senate (Second Chamber of Parliament) |
 |
|
|
Political groups
|
Confidence and supply (448)
Opposition (24)
|
 |
|
|
Political groups
|
Confidence and supply (201)
Opposition (11)
|
| Elections | |
|
Last election
|
2020 Egyptian parliamentary election |
|
Last election
|
2020 Egyptian Senate election |
|
Next election
|
2025 Egyptian parliamentary election |
|
Next election
|
2025 Egyptian Senate election |
| Meeting place | |
| People's Assembly chamber of the Egyptian Parliament building, New Administrative Capital, Egypt | |
| Website | |
| http://www.parliament.gov.eg | |
The Parliament of Egypt is like the main law-making body for the country of Egypt. It has two main parts: an upper house called the Senate and a lower house called the House of Representatives. Think of it as two teams working together to make important decisions for the country.
This important building is located in the New Administrative Capital, which is Egypt's capital city. According to Egypt's rules (its 2014 constitution), the Parliament has many big jobs. It creates new laws, agrees on the country's main plans for how things should work, and decides how the government's money will be spent. It also watches over the government's work and can even vote to remove the president or change the government and its prime minister if needed.
The Parliament has a total of 596 members. Most of these members are chosen by people voting for them. Some seats are set aside for young people, women, and other groups to make sure everyone is represented. A few members are also chosen by the president. This makes Egypt's Parliament one of the largest in the world and the biggest in the Arab world.
Contents
How Egypt's Parliament Started
Egypt has a long history of having a parliament, going all the way back to 1866! Over the years, the way the parliament worked changed many times. Different groups and systems were tried to help the people of Egypt have a say in their government and build a country based on fairness and freedom.
For more than 135 years, Egypt has had many different parliaments. These groups had different numbers of members, from 75 to 458, and they all helped shape Egypt's modern story. Today, the Parliament mainly includes the House of Representatives, which has 596 members.
Times Without a Parliament
There was a period when Egypt did not have a parliament for three years. The parliament was closed down in June 2012. Later, in 2012, President Mohamed Morsi tried to bring it back, but he was removed from his position. New elections for the parliament were finally held between October and December 2015.
How Candidates Campaign
When people run for a seat in Parliament, they need to tell voters why they should be chosen. In Egypt, candidates often visit potential voters in their homes, especially in the evenings. These visits are a way for candidates to meet people face-to-face and build trust.
During these visits, candidates might be offered drinks or sweets. They often talk with families and try to get their support. Sometimes, people will ask candidates for small favors, like help with a government office, if they get elected. This shows how important personal connections are in Egyptian elections.
Candidates usually campaign with their family members. Winning an election is often a matter of family pride. It's a way for them to show their community that they are ready to serve.
The House of Representatives Today
How Members Join the House
The rules for the House of Representatives were set in Egypt's 2014 constitution. To become a member, a person must be Egyptian, at least 25 years old, and have an education certificate. The House must have at least 450 members, and the president can choose up to five percent of them.
Members of the House usually serve for five years. However, the president can decide to end their term earlier. All members are chosen through elections where people vote for their representatives.
The House has the power to ask the government's leaders, called the cabinet, to step down if they are not doing a good job. This means the Prime Minister of Egypt and the cabinet usually come from the main political group in the House.
What the House of Representatives Does
The House of Representatives has many important jobs, as outlined in Egypt's Constitution. Here are some of its main responsibilities:
- Making new laws for the country.
- Looking at and approving agreements and treaties with other countries.
- Checking and approving the government's plans and how it will spend money.
- Talking about the president's speeches and the government's goals.
- Making changes to the Constitution, which is the country's main rulebook.
- Giving approval for important decisions like declaring war or a state of emergency.
Before the 2011 Egyptian revolution, the House of Representatives had less power. One political party had most of the control, so there wasn't much disagreement with the president's decisions.
How the House is Organized
The Speaker of the House
The Speaker is like the leader of the House of Representatives. This person is chosen by the members of the House, along with two assistants. The Speaker's main job is to make sure meetings run smoothly and in an orderly way.
If the president's position ever becomes empty, the Speaker steps in as acting president until a new president can be elected. This happened once in Egypt's history. The last Speaker was Saad Al Katatny, who led the House for a short time in 2012.
Speaker's Office Team
The Speaker has a team that helps organize all the meetings and plans for the House and its committees. They also make sure the House's decisions are followed and connect the House with other government groups.
Main Committee of the House
There is a main committee that starts working at the beginning of each year. The Speaker leads this committee, which includes other important members and representatives from different political groups. This committee talks about big issues suggested by the president, prime minister, or the Speaker.
Special Committees
The House also has many special committees that focus on different topics. These committees study specific areas in detail. Some examples include:
- Education Committee
- Health Committee
- Youth and Sports Committee
- Transport Committee
- Economic Affairs Committee
- Foreign Affairs Committee
Rules and Conduct Committee
This committee makes sure that all members of the House follow good rules of behavior and act responsibly. It looks into any issues where a member might not have followed the expected standards.
Temporary and Joint Committees
Sometimes, special temporary committees are created to study a new law or a specific problem. The Speaker chooses the members for these groups. There are also joint committees, which bring together members from different special committees to work on a particular issue. Decisions in these committees are made by a majority vote.
International Connections
The Egyptian House of Representatives also has a group that works on building good relationships with parliaments in other countries. This helps Egypt connect with the rest of the world and share ideas. The Speaker leads this group, which includes members from different political parties.
See also
 In Spanish: Parlamento de Egipto para niños
In Spanish: Parlamento de Egipto para niños
- History of the Egyptian parliament
- Politics of Egypt
- Speaker of the House of Representatives (Egypt)
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |

