Broad-leaved geebung facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Broad-leaved geebung |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Persoonia |
| Species: |
P. levis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Persoonia levis (Cav.) Domin
|
|
 |
|
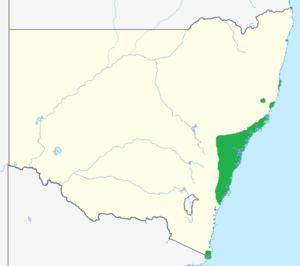
| Range of P. levis in New South Wales and extending into eastern Victoria | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The broad-leaved geebung (scientific name: Persoonia levis) is a special type of shrub or small tree. It grows naturally in New South Wales and Victoria in eastern Australia. This plant can grow up to 5 meters (16 feet) tall. It has dark grey bark that feels like paper and bright green leaves. These leaves are shaped a bit like a sickle and can be up to 14 cm (5.5 inches) long.
In summer and autumn (from December to April), the broad-leaved geebung produces small yellow flowers. After the flowers, it grows small, green, fleshy fruits. These fruits are called drupes. The broad-leaved geebung is part of a large family of plants called Persoonia. It can even mix with other similar species where they grow close together.
This plant lives in dry sclerophyll forests, usually on sandstone soil that doesn't have many nutrients. It's very good at surviving bushfires. After a fire, new shoots can grow from under its thick bark. These plants can live for more than 60 years! New plants can also grow from seeds hidden in the soil after a fire. Bees, like the longtongue bee, help pollinate its flowers. Animals like kangaroos, possums, and currawongs enjoy eating its fruit. Even though it's a beautiful plant, it's hard to grow in gardens because its seeds are tricky to sprout and cuttings don't easily take root.
Contents
What Does It Look Like?
The broad-leaved geebung grows as a tall shrub or a small tree. It can reach about 5 meters (16 feet) in height. Its bark is dark grey on the outside and feels soft and flaky. If you look deeper, the bark layers are reddish. Inside this bark are special buds that can sprout new growth after a bushfire.
The new branches are usually smooth or slightly hairy. The leaves are large and bright green, measuring 6 to 14 cm (2.2–5.5 inches) long. They are often oblong or shaped like a sickle. This uneven shape helps tell it apart from a similar plant called P. lanceolata. The bright green leaves, especially the new ones, stand out against the reddish stems and other plants around them.
Yellow flowers bloom in summer and autumn, mostly from December to February. They grow in small clusters along the branches. Each flower has both male and female parts. The fruit is smooth, green, and round, about 1 cm (0.4 inches) across. It's a fleshy fruit called a drupe and contains two seeds. The fruit is juicy but can be stringy when not ripe. The seeds and skin are not meant to be eaten.
Where Does It Grow?

You can find the broad-leaved geebung from the Macleay River area in New South Wales all the way to the Cann River in eastern Victoria. It prefers dry sclerophyll forests where the soil is sandy and doesn't have many nutrients. It grows in sunny or partly shaded spots in open woodlands.
It often grows alongside other Australian trees like Eucalyptus piperita, E. sieberi, and Angophora costata. It also shares its home with shrubs like Grevillea buxifolia and the beautiful Telopea speciosissima (Waratah). Plants growing near the coast tend to be smaller with wider leaves than those found further inland.
This plant is well-protected in the Sydney area. You can find it in many national parks, including Georges River National Park, Wollemi National Park, and Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park.
How It Lives and Survives
The broad-leaved geebung is very good at surviving bushfires. It's one of several Persoonia species that can regrow from its trunk after a fire. Its thick, papery bark protects the hidden buds from the flames. New plants also grow from seeds that are stored in the soil, sometimes taking up to a year to sprout after a fire. These plants can live for more than 60 years!
Tiny fungi called mycorrhiza have been found on the roots of the broad-leaved geebung. These fungi help the plant get nutrients from the soil. However, a fungal disease called leaf spot can affect the plant. The larvae (young stage) of a weevil insect called Eurhynchus laevior also feed on this plant.
Special bees, like the Leioproctus carinatifrons (a type of longtongue bee), are very important for pollinating the broad-leaved geebung's flowers. These bees visit the flowers to collect food and, in doing so, help the plant make seeds. The fruit of the broad-leaved geebung is eaten by animals like kangaroos, possums, and large birds such as currawongs. The flowers of the broad-leaved geebung cannot fertilize themselves; they need pollen from another plant to produce seeds.
Growing Broad-leaved Geebung
It's quite rare to see the broad-leaved geebung grown in gardens. This is mainly because it's very hard to grow new plants from its seeds, and taking cuttings almost never works. However, its colorful bark and bright green leaves make it a very attractive plant for gardens.
If you want to try growing one, it needs sandy soil that drains well, and a spot that gets sun or partial shade. Once it's established, it can handle moderate frosts and dry periods. It grows fairly well, though slowly, if the conditions are right. People in England managed to sprout its seeds as early as 1795!


