Polymerization facts for kids
Polymerization is a cool process where tiny building blocks, called monomers, link up to create super-long chains or networks. These big chains are called polymers. Think of it like snapping together many small LEGO bricks to build a giant LEGO structure!
The small molecules (monomers) can all be the same, or they can be different kinds of molecules. To make a real polymer, you usually need at least 100 monomer molecules to join. When they do, the new material gets special features. It might become stretchy, super strong, or able to form fibres, like the threads in your clothes. Often, thousands of these tiny units connect to form just one polymer molecule!
This linking happens because the monomers form strong chemical bonds with each other. This is different from things like crystallization, where molecules just stick together loosely.
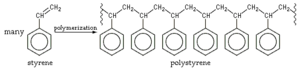
One common way polymers are made is from alkene molecules. These are special molecules that can react with themselves in a process called "addition polymerization." This is how many plastics are made! When you add a catalyst (a substance that speeds up chemical reactions) or heat the alkenes under pressure, their double bonds break open. This allows them to link up, one after another, forming a long polymer chain.
What are polymers used for?
Polymers are all around us! One very common polymer is polyethene. It's a cheap and super useful plastic. You've probably seen it used for plastic bags, bottles, and many other everyday items. It's popular because it's flexible and quite strong.
Images for kids
-
Polymerization of ethylene
See also

 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |

