Apoptosis facts for kids
Apoptosis is a process of programmed cell death. It occurs in multicellular organisms, including humans, animals, and plants. While the idea of cells dying might sound bad, apoptosis is actually a very important and healthy part of life. It allows the body to remove old, damaged, or unnecessary cells in a neat and controlled way.
Unlike necrosis, which is accidental cell death caused by an injury or poison, apoptosis is a planned event. The cell breaks itself down carefully so that it does not damage the cells around it. For example, the average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For a child between 8 and 14 years old, about 20 to 30 billion cells die every day to make room for new ones.
Contents
What is Apoptosis?
The word apoptosis comes from Ancient Greek words meaning "falling off" (Ancient Greek: ἀπόπτωσις). It refers to the way leaves fall from a tree in autumn. Just as trees shed leaves to stay healthy, our bodies shed cells.
Scientists first described this process in the 19th century. However, it was not until the 1970s that researchers fully understood how important it is. In 2002, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Sydney Brenner, H. Robert Horvitz, and John Sulston for their discoveries about how genes control this process.
How Apoptosis Works
Apoptosis is a highly regulated process. It is like a complex machine that can be turned on when needed. Because the cell cannot stop the process once it starts, there are strict safety checks in place.
Internal and External Triggers
There are two main ways a cell decides to undergo apoptosis:
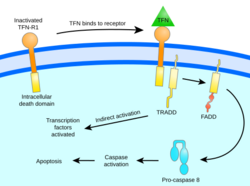
- The Intrinsic Pathway (Internal): This happens when a cell senses stress from the inside. For example, if a cell's DNA is damaged beyond repair, it will trigger its own death. The mitochondria, which are the energy centers of the cell, play a key role here by releasing specific proteins.
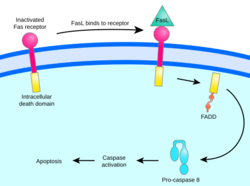
- The Extrinsic Pathway (External): This happens when a cell receives signals from other cells in the body. These signals bind to "death receptors" on the surface of the cell, telling it that it is time to shut down.
The Demolition Crew
Once the signal is given, the cell activates special enzymes called caspases. You can think of caspases as a demolition crew or a pair of molecular scissors. They cut up the proteins and structures inside the cell.
- Initiator caspases are the first to be activated. They act like the foreman giving orders.
- Executioner caspases do the actual work of breaking down the cell parts.
Cleaning Up
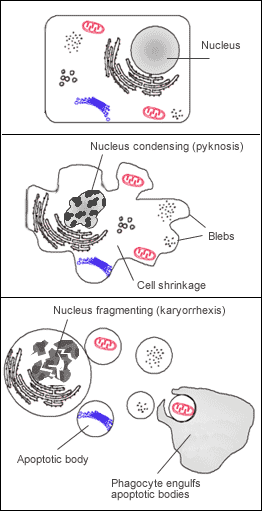
As the cell breaks down, it goes through several changes:
- The cell shrinks and pulls away from its neighbors.
- The DNA inside the nucleus is chopped into small pieces.
- The cell breaks into smaller fragments called apoptotic bodies.
Finally, special immune cells called phagocytes (meaning "eating cells") come along and engulf these fragments. This prevents any harmful substances from leaking out and damaging nearby healthy cells. This process is very clean and does not cause inflammation.
Why is Apoptosis Important?
Apoptosis is essential for the survival and health of an organism. It serves two main purposes: building the body and protecting it.
Growth and Development
During development, apoptosis acts like a sculptor's chisel, removing extra material to create the correct shape.
- Fingers and Toes: In a human embryo, the hands and feet start as paddle-like shapes. Apoptosis kills the cells between the fingers and toes, allowing them to separate.
- Metamorphosis: When a tadpole turns into a frog, apoptosis causes the cells in its tail to die, so the tail disappears as the frog grows legs.
- Brain Development: The brain produces many more neurons than it needs. Apoptosis removes the ones that do not form proper connections.
Protecting the Body
Apoptosis is a defense mechanism. It removes cells that could be dangerous to the rest of the body.
- Damaged Cells: If a cell has damaged DNA caused by radiation or chemicals, it could turn into a cancer cell. Apoptosis destroys these cells before they can grow out of control.
- Infected Cells: When a cell is infected by a virus, the body's immune system can command that cell to die. This stops the virus from replicating and spreading to other cells.
Apoptosis and Disease
Because apoptosis is so powerful, it must be perfectly balanced. If there is too much or too little cell death, it can lead to disease.
Too Little Apoptosis
If apoptosis does not work correctly, cells that should die continue to live and divide. This is a major cause of cancer.
- Cancer: Cancer cells often have mutations that turn off the apoptosis machinery. This allows them to grow into tumors and ignore signals that tell them to stop dividing.
- Viruses: Some viruses, like the human papillomavirus (HPV), produce proteins that block apoptosis. This keeps the infected cell alive so the virus can continue to make copies of itself.
Too Much Apoptosis
If apoptosis happens too often, the body loses healthy cells that it needs.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: In diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, nerve cells in the brain die when they shouldn't. This leads to a loss of memory and control over movement.
- HIV and AIDS: The HIV virus attacks the immune system. It causes helper T-cells to undergo apoptosis too quickly. Without enough of these cells, the body cannot fight off infections.
How Scientists Study Apoptosis
Scientists use special tools to tell the difference between apoptosis and other types of cell death.
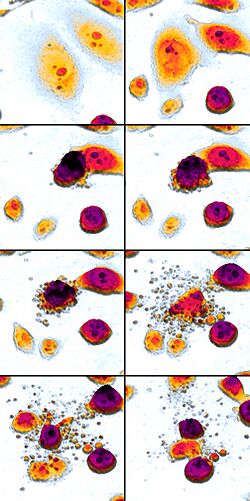
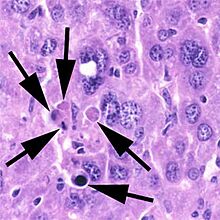
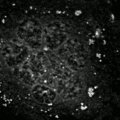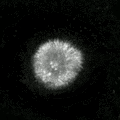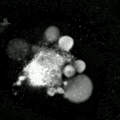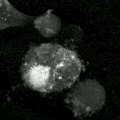
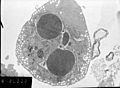
- Microscopes: They can look for physical signs, like the cell shrinking or the nucleus breaking apart.
- DNA Ladders: Because apoptosis cuts DNA into specific sizes, scientists can see a "ladder" pattern when they analyze the DNA in a gel.
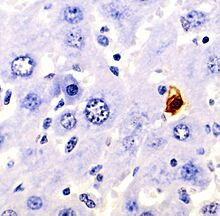
- Staining: Special dyes can be used to color cells that are undergoing apoptosis, making them visible under a microscope.
See also
 In Spanish: Apoptosis para niños
In Spanish: Apoptosis para niños
Images for kids