Puabi facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Puabi𒅤𒀀𒉿 |
|
|---|---|
| Queen of Ur | |

Queen Puabi seated, with attendants, c. 2600 BCE
|
|
| Reign | fl. c. 2600 BCE |
| House | First Dynasty of Ur |
Puabi was an important woman who lived in the ancient Sumerian city of Ur around 2600 BCE. This was during a time known as the First Dynasty of Ur. Her name, Puabi, means "Word of my father" in the Akkadian language. She is often called a "queen," and some special seals found in her tomb use Sumerian words like "nin" or "eresh," which mean queen or priestess.
What's interesting is that Puabi's own seal doesn't mention her being married to a king. This might mean she ruled on her own. Some experts think she might have been the second wife of King Meskalamdug. Puabi was from the Semitic Akkadian people, but she was very important among the Sumerians. This shows how much different cultures mixed and influenced each other back then. We don't know much about Puabi's daily life, but her tomb has taught us a lot about ancient Mesopotamian society.
Contents
Discovering Puabi's Ancient Tomb
A British archaeologist named Leonard Woolley found Puabi's tomb. His team, which included his wife and fellow archaeologist, Katharine Woolley, worked on the excavation between 1922 and 1934. They were sponsored by the British Museum and the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. Katharine Woolley even drew detailed maps of the site.
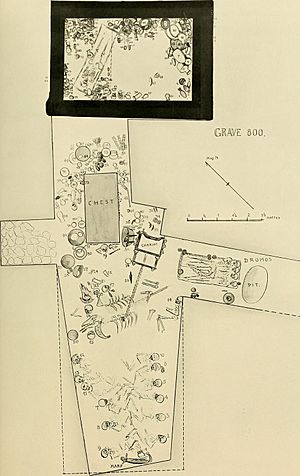
Puabi's tomb was one of about 1,800 graves found at the Royal Cemetery in Ur. Her tomb was special because it had never been robbed. This meant all the amazing treasures inside were still there, perfectly preserved after thousands of years.
Treasures Found in Puabi's Tomb
The amount of valuable items Woolley found in Puabi's tomb was incredible. These included:
- A magnificent, heavy golden headdress decorated with golden leaves, rings, and plates.
- A beautiful lyre (a type of harp) with a golden and lapis lazuli (a blue stone) bull's head.
- Lots of gold tableware, like plates and cups.
- Many necklaces and belts made from gold, carnelian (a red-orange stone), and lapis lazuli beads.
- A chariot decorated with silver lioness heads.
- Plenty of silver, lapis lazuli, and gold rings and bracelets.
Puabi's headdress was inspired by nature, with designs of flowers, gold ribbons, and leaves.
The Mystery of the "Death Pits"
Outside and above Puabi's burial chamber, archaeologists found several "death pits." These pits have raised questions about whether they were directly linked to Puabi.
The largest pit contained the remains of 74 people: 6 men and 68 women. All of them wore gold, silver, and lapis lazuli decorations. One woman seemed to have even more elaborate jewelry than the others. Another pit, found above Puabi's chamber, held 21 people, a fancy harp or lyre, a chariot, and a large chest of personal grooming items.
It's still not fully clear if these pits were directly connected to Puabi's burial.
Understanding How People Died
Scientists have used CAT scans to study some of the remains from these pits. The scans suggest that some people died from a strong blow to the head. A pointed, weighted tool found by Woolley could have caused the skull damage seen. A small hammer-like tool was also found.
Some remains also showed traces of cinnabar, a substance that would have been used to slow down the bodies' decay. This would have allowed time for important funeral ceremonies to be completed.
Where Puabi's Remains and Treasures Are Now
Puabi's physical remains, including parts of her skull, are kept at the Natural History Museum, London. The treasures found during Woolley's expedition were shared among three places:
- The British Museum in London.
- The University of Pennsylvania Museum in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
- The National Museum in Baghdad, Iraq.
Sadly, some of the treasures from the National Museum in Baghdad were stolen after the Second Gulf War in 2003. Many of the most amazing pieces from Puabi's tomb have been shown in popular art and history museum tours in the United Kingdom and the United States.
Artefacts from Puabi's Tomb
See also
 In Spanish: Puabi para niños
In Spanish: Puabi para niños
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |