Pyramid of Neferirkare facts for kids
The Pyramid of Neferirkare is an ancient Egyptian pyramid. It was built for Pharaoh Neferirkare Kakai. He was a ruler during Egypt's Fifth Dynasty. This was around 2500 BC.
This pyramid was the tallest building in the necropolis of Abusir. This area is located between the famous sites of Giza and Saqqara. Even today, it stands tall over the other ancient structures. The pyramid is also important because its discovery led to finding the Abusir Papyri. These are ancient Egyptian writings.
The Fifth Dynasty saw the end of the very large pyramid constructions. These were common during the Old Kingdom. Pyramids from this time became smaller. They also followed more standard designs. However, they still had beautiful carvings and decorations.
Contents
A Unique Pyramid Design
Neferirkare's pyramid was different from others of its time. It was first planned as a step pyramid. This type of design was old-fashioned. It had been popular much earlier, during the Third Dynasty. That was around 2600 or 2700 BC.
Building Challenges and Changes
Pharaoh Neferirkare died before his pyramid was finished. His successors had to complete the work. They finished the remaining parts very quickly. They also used less expensive building materials. Because of this rush, Neferirkare's monument was missing some key parts. These included a valley temple, a special pathway called a causeway, and a smaller cult pyramid.
Nearby Monuments
Other important monuments are located around Neferirkare's pyramid. These include tombs for his wife, Khentkaus II. There are also monuments for his sons, Neferefre and Nyuserre Ini.
Images for kids
-
1907 painting of the Abusir necropolis, by A. Bollacher and E. Decker, presented as it was in the Old Kingdom
-
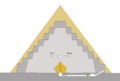
The three stages of the pyramid's construction. Light grey: original six step core of the planned step pyramid. Dark grey: extension project with two extra steps. Beige: planned granite casing. Internally, the corridor and three layer limestone gable roof of the ante- and burial- chamber are also depicted.
-
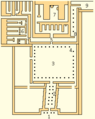
Layout of Neferirkare's mortuary temple. In order: (1) entry portico; (2) entry hall; (3) courtyard with (4) wooden columns; (5) transverse corridor; (6) storerooms, notable for the Abusir papyri found there; (7) inner temple; (8) columned corridor leading to (9) a passageway into the main courtyard.
See also
 In Spanish: Pirámide de Neferirkara para niños
In Spanish: Pirámide de Neferirkara para niños