Saqqara facts for kids
|
سقارة
|
|

The stepped Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara
|
|
| Location | Giza Governorate, Egypt |
|---|---|
| Region | Lower Egypt |
| Coordinates | 29°52′16″N 31°12′59″E / 29.87111°N 31.21639°E |
| Type | Necropolis |
| History | |
| Periods | Early Dynastic Period to Middle Ages |
| Site notes | |
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
| Part of | "Pyramid fields from Giza to Dahshur" part of Memphis and its Necropolis – the Pyramid Fields from Giza to Dahshur |
| Includes |
|
| Criteria | Cultural: (i), (iii), (vi) |
| Inscription | 1979 (3rd Session) |
| Area | 16,203.36 ha (62.5615 sq mi) |
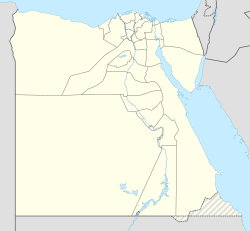
Saqqara (Arabic: سقارة) is a huge, ancient burial ground in Egypt. It stretches about 7 kilometers long and 1.5 kilometers wide. This was the main burial place, also called a necropolis, for the ancient Egyptian capital city of Memphis.
Saqqara is home to many pyramids, including the famous Pyramid of Djoser. This pyramid is sometimes called the Step Tomb. It has a rectangular base and looks like it has giant steps. These steps are actually layers of flat, bench-like structures called mastabas. Saqqara is located about 30 kilometers south of modern-day Cairo.
The Pyramid of Djoser is the oldest complete stone building complex known in history. It was built during the Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt. After Djoser, 16 other Egyptian kings also built pyramids at Saqqara. Many of these pyramids are now partly damaged or have fallen apart. Important officials also built their private tombs here for over 3,000 years. This continued into the Ptolemaic and Roman times.
Contents
Why is Saqqara Important?
The area from Giza to Dahshur was named a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1979. This means it's a very special place that needs to be protected. The official name for this site is "Memphis and its Necropolis – the Pyramid Fields from Giza to Dahshur."
Some experts believe the name 'Saqqara' comes from a local tribe called Beni Saqqar. Others think it might be named after an ancient Egyptian god of funerals, Sokar.
What Can You See at Saqqara?
Saqqara is like a giant outdoor museum. You can explore many different types of ancient Egyptian structures here. These include pyramids, tombs, and other buildings. Each one tells a story about the people who lived in ancient Egypt.
The Step Pyramid of Djoser
The Pyramid of Djoser is the most famous structure at Saqqara. It was designed by the brilliant architect Imhotep. This pyramid was a huge step forward in building. Before it, tombs were mostly flat, rectangular structures. Djoser's pyramid showed that Egyptians could build much bigger and taller monuments using stone.
Other Pyramids and Tombs
Besides Djoser's pyramid, many other kings built their tombs here. You can see pyramids from different periods of ancient Egyptian history. High-ranking officials and their families also had their burial places at Saqqara. These tombs often have amazing carvings and paintings inside. They show scenes of daily life, religious rituals, and journeys to the afterlife.
The Serapeum of Saqqara
One unique site is the Serapeum of Saqqara. This was a burial place for sacred bulls. Ancient Egyptians believed these bulls were living forms of the god Apis. The Serapeum has long underground tunnels with huge stone sarcophagi (coffins) for the bulls. It's a fascinating look into their religious beliefs.
Images for kids
-
View of Saqqara necropolis, including Djoser's step pyramid (centre), the Pyramid of Unas (left) and the Pyramid of Userkaf (right)
-
Wooden statue of the scribe Kaaper, 4th or 5th dynasty of the Old Kingdom, from Saqqara, c. 2500 BC
See also
 In Spanish: Saqqara para niños
In Spanish: Saqqara para niños