Lower Egypt facts for kids
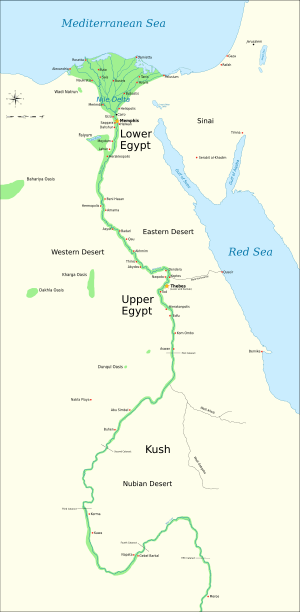
Lower Egypt was an important part of Ancient Egypt. It was the northern region of the country. This area stretched from the Mediterranean Sea south to near modern-day Cairo. It included the rich, fertile land of the Nile Delta. The Nile Delta is where the Nile River splits into many branches. These branches spread out like a fan before reaching the sea. This created a very fertile area, perfect for farming.
Lower Egypt was also known as Ta-Mehu. This name means "land of papyrus." Papyrus was a tall plant that grew in wet areas. Ancient Egyptians used it to make paper, boats, and other things.
Contents
Geography and Climate
The land in Lower Egypt was mostly undeveloped scrubland. This means it had many wild plants like grasses and herbs. It was not always easy for people to live there.
The climate in Lower Egypt was milder than in Upper Egypt. Temperatures were not as extreme. There was also more rainfall, which helped the plants grow.
Important Features of Lower Egypt
The capital city of Lower Egypt was Buto. This city was very important for the region.
Lower Egypt had a special protector. This was the cobra goddess Wadjet. She was seen as the guardian of the land.
The rulers of Lower Egypt wore a unique crown. It was called the Low Red Crown, or Deshret. This crown was a strong symbol of their power. The main symbol for Lower Egypt itself was the papyrus plant.
Related Places
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bajo Egipto para niños
In Spanish: Bajo Egipto para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |