Shingle oak facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Shingle oak |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Quercus
|
| Species: |
imbricaria
|
 |
|
| Natural range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
Erythrobalanus imbricaria (Michx.) O.Schwarz
Quercus aprica Raf. Quercus imbricaria var. inaequalifolia Kuntze Quercus imbricaria var. spinulosa A.DC. Quercus latifolia Steud. Quercus phellos var. imbricaria (Michx.) Spach Quercus phellos var. imbricaria (Michx.) A.DC. Quercus sonchifolia Booth ex Petz. & G.Kirchn. |
|
The shingle oak, also known by its scientific name Quercus imbricaria, is a type of deciduous tree. This means it loses its leaves every year. It belongs to the red oak group of oak trees.
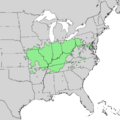
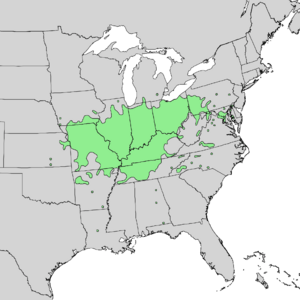
You can find the shingle oak mainly in the Midwestern and Upper South parts of North America. Its natural home stretches from southern New York west to northern Illinois and eastern Kansas. It also grows south into central Alabama and Arkansas. This tree usually grows on high ground with good drainage. Sometimes, it can be found near streams in lower areas. It typically grows at heights of 100 to 700 meters (about 330 to 2,300 feet) above sea level.
The shingle oak is a medium-sized tree. It can grow up to 20 meters (about 67 feet) tall. Its trunk can be as wide as 1 meter (about 40 inches) across. What makes this oak special are its leaves. They look like the leaves of a Bay laurel plant. They are long and narrow, about 8–20 cm (4–10 inches) long and 1.5–7.5 cm (0.6–3.0 inches) wide. The edges of the leaves are smooth, without any teeth or lobes. The top of the leaf is bright green, while the underside is paler and a bit fuzzy.
The fruit of the shingle oak is an acorn. These acorns are small, about 9–18 mm (0.35–0.7 inches) long and wide. They have a shallow cup at their base. It takes about 18 months for the acorns to fully grow after the tree is pollinated. Shingle oak acorns are an important food source for animals. Many squirrels and some birds love to eat them.
Contents
What Does a Shingle Oak Look Like?
A shingle oak tree often grows to be 15–18 meters (50–60 feet) tall. Some can even reach 30 meters (100 feet). When they are young, they have a wide, pyramid shape. As they get older, their top becomes wider and more open. While not common in the eastern parts of the U.S., they are very common in the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys. The biggest shingle oaks are found in southern Illinois and Indiana.
Bark and Wood
The bark of the shingle oak is light brown and has scales. On younger branches, the bark is smooth and light brown. The smaller branches are dark green and shiny at first. Later, they turn light brown, then dark brown.
The wood of the shingle oak is pale reddish-brown, with lighter sapwood. It is heavy, hard, and has a coarse grain. In the past, this wood was very important for making shingles. This is how the tree got its common name, "shingle oak." It was also sometimes used in building.
Leaves and Flowers
The leaves of the shingle oak grow alternately along the branch. They are oblong or oval-shaped. They are usually 10–15 cm (4–6 inches) long and 2.5–5 cm (1–2 inches) wide. The base of the leaf can be wedge-shaped or rounded. The tip can be pointed or rounded. Sometimes, the edges are smooth, or they might be slightly wavy.
When the leaves first appear, they are bright red and rolled up. They have a rusty fuzz on top and white fuzz underneath. When they are fully grown, the top is dark green, smooth, and shiny. The underside is pale green or pale brown and fuzzy. In the autumn, the leaves turn dark red on top and stay pale underneath.
The shingle oak flowers in May, when its leaves are about half grown. The male flowers grow on fuzzy hanging clusters called aments. The female flowers grow on thin, fuzzy stalks.
Acorns and Life Cycle
The acorns of the shingle oak take two years to fully ripen. They can grow alone or in pairs on a stalk. The nut part of the acorn is almost round. It is about 1.2–1.7 cm (0.5–0.66 inches) long. The cup covers about half to two-thirds of the nut. This cup is covered with light reddish-brown, fuzzy scales. The kernel inside the acorn is very bitter.
Shingle Oak Hybrids
Sometimes, the shingle oak can naturally cross with other oak trees. When this happens, it creates a hybrid tree. One example is Quercus × leana, also known as Lea's hybrid oak. This tree is a mix of the black oak (Q. velutina) and the shingle oak (Q. imbricaria). Lea's hybrid oak can grow up to 20 meters (67 feet) tall. It is found naturally in southeastern North America.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Quercus imbricaria para niños
In Spanish: Quercus imbricaria para niños