Reticulated python facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Reticulated pythonTemporal range: Pleistocene to recent
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Unrecognized taxon (fix): | Malayopython |
| Species: |
Template:Taxonomy/MalayopythonM. reticulatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Template:Taxonomy/MalayopythonMalayopython reticulatus (Schneider, 1801)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
Boa reticulata
Schneider, 1801 Boa rhombeata Schneider, 1801 Boa phrygia Shaw, 1802 Coluber javanicus Shaw, 1802 Python schneideri Merrem, 1820 Python reticulatus — Gray, 1842 Python reticulatus — Boulenger, 1893 Morelia reticulatus — Welch, 1988 Python reticulatus — Kluge, 1993 Broghammerus reticulatus — Hoser, 2004 Malayopython reticulatus — Reynolds et al., 2014 |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The reticulated python (Malayopython reticulatus) is a giant snake species that lives in South and Southeast Asia. It is famous for being the world's longest snake and the third heaviest. This snake is not venomous. Instead, it is a constrictor, which means it squeezes its prey.
Reticulated pythons are excellent swimmers. They have been seen far out at sea, which has helped them travel to and live on many small islands. Because they are found in so many places, they are listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List, meaning they are not in danger of extinction. In some countries, these pythons are hunted for their skin or for use in traditional medicine. They are also sometimes sold as pets.
Contents
Naming and Types
The reticulated python was first given its scientific name in 1801. Its species name, reticulatus, is Latin for "net-like." This name was chosen because of the beautiful, complex pattern on its skin that looks like a net.
Over the years, scientists have studied this python and its relatives to figure out how they are related. This led to changes in its genus name, but today it is most commonly known as Malayopython reticulatus.
Different Kinds of Reticulated Pythons
Scientists have identified a few different types, or subspecies, of reticulated pythons. Two of these are known as "dwarf" subspecies because they do not grow as large as other reticulated pythons.
- M. r. jampeanus: This is a dwarf subspecies from the island of Tanahjampea. It usually doesn't grow much longer than 2 m (6 ft 7 in).
- M. r. saputrai: This subspecies lives on Selayar Island and nearby parts of Sulawesi. It is also smaller, not growing longer than 4 m (13 ft 1 in).
These smaller pythons are a result of insular dwarfism, where animals on islands evolve to be smaller over time.
What Does It Look Like?
The reticulated python has smooth scales and a very complex geometric pattern on its back. This pattern is usually made of diamond shapes with lighter centers. The colors and markings can be very different depending on where the snake lives.
This pattern might look bright and easy to see in a zoo, but it is great camouflage in the jungle. Among fallen leaves and shadows, the snake can become almost invisible. This helps it hide from predators and ambush its prey.
How Big Can It Get?
The reticulated python is the longest snake in Asia. Most wild pythons are between 1.5 to 6.5 m (4 ft 11 in to 21 ft 4 in) long. It is rare to find one longer than 6 m (19 ft 8 in), but it does happen. According to the Guinness Book of World Records, this is the only snake species that regularly grows longer than that.
Measuring a live giant snake is very difficult. They are incredibly strong, and they don't stay straight. Because of this, many old reports of super-long snakes are thought to be exaggerated.
- A reticulated python in Kansas City, Missouri, named "Medusa" holds the Guinness World Record for the longest snake ever kept in captivity. In 2011, she measured 7.67 m (25 ft 2 in) and weighed 158.8 kg (350 lb 2 oz).
There are also "super dwarf" reticulated pythons that come from small islands. These are popular as pets because they only grow to between 1.82 and 2.4 m (6 ft 0 in and 7 ft 10 in).
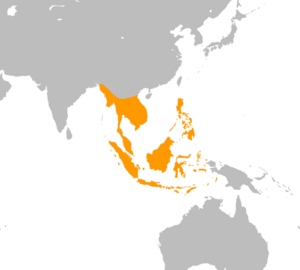
Where Does It Live?
The reticulated python is found all across South and Southeast Asia. It lives in many countries, including:
- India
- Bangladesh
- Myanmar
- Thailand
- Laos
- Cambodia
- Vietnam
- Malaysia
- Singapore
- Indonesia
- The Philippines
This snake prefers to live in rainforests, woodlands, and grasslands. It is often found near rivers, streams, and lakes. It is such a good swimmer that it has spread to many small islands throughout its range. It has even been found in busy cities like Bangkok.
How Does It Behave?
Hunting and Diet
Like all pythons, the reticulated python is an ambush predator. It hides and waits for prey to come close. When an animal is within range, the python strikes, grabs it, and quickly wraps its coils around it, killing it by constriction.
Its diet includes mammals and sometimes birds.
- Young pythons (up to 3–4 m (9 ft 10 in – 13 ft 1 in) long) eat small animals like rats, bats, and treeshrews.
- Larger pythons hunt bigger prey like civets, primates, pigs, and even deer.
A reticulated python can swallow prey up to one-quarter of its own length and as heavy as itself. When living near people, they have been known to eat chickens, cats, and dogs.
Life Cycle
The reticulated python is oviparous, which means it lays eggs. A female can lay between 15 and 80 eggs at a time. She will coil around her eggs to protect them and keep them warm. The eggs take about 88 days to hatch. The baby snakes are already at least 2 ft (0.61 m) long when they are born.
Relationship with Humans
Reticulated pythons are wild animals and should be treated with respect. Because they are so large and powerful, they can be dangerous. Attacks on people are extremely rare, as these snakes usually prefer to stay away from humans.
However, there have been a few confirmed cases where very large pythons have attacked people. This is why it is important to be careful in areas where they live and to never approach one in the wild.
Reticulated Pythons as Pets
The reticulated python has become a popular pet, partly because of selective breeding. Breeders have created many different color and pattern variations called "morphs," with names like "Albino," "Tiger," and "Sunfire."
The smaller "super dwarf" pythons are also popular because they are easier to handle. Even so, a reticulated python is a big responsibility. Because of their great size and strength, they should only be kept by experienced reptile keepers who can provide for their needs and handle them safely.
See also
 In Spanish: Pitón reticulada para niños
In Spanish: Pitón reticulada para niños
- List of largest snakes
- Burmese python