Scorpius–Centaurus association facts for kids
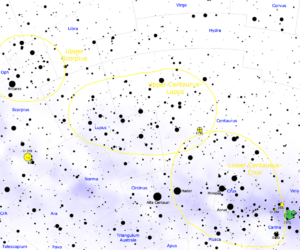
The Scorpius–Centaurus association, often called Sco–Cen, is the closest group of young, massive stars to our Sun. It's like a cosmic neighborhood of stars that were born around the same time. This huge group is made up of three smaller parts: Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux. Sco–Cen is about 130 parsecs away, which is about 420 light-years. Scientists have found at least 436 stars that belong to this association. They used special data from the Hipparcos satellite to study these stars.

Contents
How Old Are the Stars in Sco-Cen?
The different parts of the Sco–Cen association have slightly different ages. The Upper Scorpius group is the youngest, at about 11 million years old. The Upper Centaurus–Lupus and Lower Centaurus–Crux groups are a bit older, around 15 million years old.
Many bright stars you see in the night sky are part of Sco–Cen. These include stars in the constellations Scorpius, Lupus, Centaurus, and Crux. For example, Antares, a very massive star in Scorpius, is a member. Most of the stars in the famous Southern Cross are also part of this group.
Scientists have found hundreds of stars in Sco-Cen. Their sizes range from very big, like Antares (about 15 times the mass of our Sun), to very small, like brown dwarfs. Brown dwarfs are objects that are too big to be planets but too small to be stars. Each of the three subgroups likely has between 1,000 and 2,000 stars.
Star-Forming Regions Near Sco-Cen
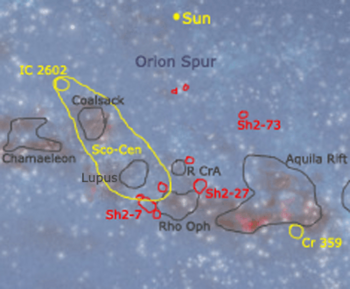
The Sco–Cen OB association is a very active area where new stars are forming. It's part of a much larger region where stars have been born recently (in the last 20 million years) and are still being born. This area contains several large clouds of gas and dust, which are like nurseries for stars. These clouds include the Rho Oph, Pipe Nebula, Barnard 68, Chamaeleon, Lupus, Corona Australis, and Coalsack cloud complexes. They are all located about 120 to 200 parsecs away.
There are also other younger star groups around Sco–Cen. These include:
- The Epsilon Chamaeleontis group, which is about 3 to 5 million years old.
- The Eta Chamaeleontis moving group, about 7 million years old.
- The TW Hydrae association, about 8 million years old.
- The Beta Pictoris moving group, about 12 million years old.
- Possibly the IC 2602 open cluster, which is around 30 to 50 million years old.
How Stars in Sco-Cen Move
The stars in the Sco–Cen association all move in a similar direction. They travel at about 20 kilometers per second (about 12 miles per second) compared to our Sun. This means they are moving almost parallel to each other. The stars within each subgroup move very closely together, only differing by 1 to 2 kilometers per second. This group of stars is likely not held together by gravity anymore, meaning they are slowly drifting apart.
Over the last 15 million years, several giant star explosions, called supernovae, have happened in Sco–Cen. These explosions created huge bubbles of expanding gas around the group, like the Loop I Bubble.
Sco-Cen and Earth's Past
Scientists have found a special type of radioactive iron (called 60Fe) in deep ocean rocks and tiny magnetic crystals. This iron might have come from a nearby supernova explosion. Some scientists think a supernova, possibly from Sco–Cen, exploded close to our Sun about 3 million years ago. This event might have even caused a small extinction event in the oceans around that time. However, other studies suggest this supernova was too far away (more than 100 parsecs) to have caused such an event through harmful UV radiation.
In 2019, researchers found interstellar iron in Antarctica. They think this iron is related to the Local Interstellar Cloud, which might have formed near the Sco-Cen association.
Planets Discovered in Sco-Cen
In December 2021, about 70 new rogue planets were found in the Upper Scorpius part of the association. Rogue planets are planets that do not orbit a star.
The Sco-Cen association is also home to some of the youngest exoplanets ever found. These are planets that pass in front of their stars, causing a dip in the star's brightness. Some examples include:
- K2-33 b (11 million years old)
- TOI-1227 b (11 million years old)
- HIP 67522 b (17 million years old)
It also contains exoplanets that have been directly photographed, such as UScoCTIO 108 b and the planets in the PDS 70 system.
See also
 In Spanish: Asociación estelar de Scorpius-Centaurus para niños
In Spanish: Asociación estelar de Scorpius-Centaurus para niños
- List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups
- β Pictoris moving group
- Ursa Major Moving Group