Siege of Menin (1706) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Siege of Menin |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of War of the Spanish Succession | |||||||
 |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Grand Alliance | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Count de Caraman Marquis de Bully |
|||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 30.000 men | 5.500 men | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 546 killed,1701 wounded 3.000 killed or wounded |
1.000 killed or wounded | ||||||
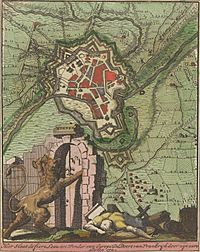
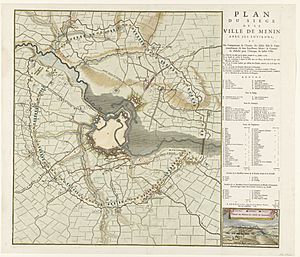
The Siege of Menin (1706) was a siege by the Allies against the French during the War of the Spanish Succession.
Siege
In the wake of the Allied victory over the French at the Battle of Ramillies on 23 May 1706, many cities across the Spanish Netherlands rapidly surrendered to the Duke of Marlborough's victorious forces. On 17 June, Kortrijk was occupied, just 11 Kilometer from the French border.
Menin had been occupied by the French since 1678 and turned into a formidable fortress by Vauban. The fortress was manned by some 5.000 French soldiers under command of general de Caraman and military governor Louis d'Etendart, Marquis de Bully.
Marlborough detached Dutch and British forces and gave the command to Ernst Wilhelm von Salisch, a Silesian general in Dutch service. On 18 July, the enemy was chased from the Counterscarp at a high cost. The next weeks, trenches were dug to the left and the right of the city towards the wall, while the city was constantly bombed. The wall was breached in the morning of 21 August, after which the French commanders asked to negotiate.
The next day, the capitulation was signed, allowing the remaining French troops to leave the city with their arms and flags, and march to Lille and Douai in France.
The damage to the city was enormous. The Sint-Vedastus church, the town hall and the monasteries of the Benedictines and the Capuchins lay in ruins. The Belfort was also partly destroyed.