Smeagol (gastropod) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Smeagol |
|
|---|---|
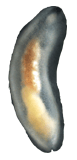 |
|
| A photo of Smeagol species | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Superfamily: |
Otinoidea
|
| Family: |
Ellobiidae
Pfeiffer, 1854
|
| Genus: |
Smeagol
Climo, 1980
|
| Diversity | |
| 5 or 6 species | |
Smeagol is a group of small, air-breathing sea slugs. They live in the upper part of the intertidal zone, which is the area of the seashore between high and low tide marks. These slugs are a type of mollusk and are related to land slugs and snails.
Scientists have studied the DNA of Smeagol slugs. This research shows that they belong to a family called Ellobiidae. This means they are closely related to other snails in that family.
Contents
Where Did the Name Come From?
The name Smeagol comes from a famous character. It is named after Sméagol, also known as Gollum. This character was created by the author J. R. R. Tolkien.
Types of Smeagol Slugs
There are five known types, or species, of Smeagol slugs. There might also be one more species found in Tasmania that has not yet been officially named.
Here are the known species:
- Smeagol climoi Tillier & Ponder, 1992
- Smeagol hilaris Tillier & Ponder, 1992
- Smeagol manneringi Climo, 1980
- Smeagol parvulus Tillier & Ponder, 1992
- Smeagol phillipensis Tillier & Ponder, 1992
How Smeagol Slugs Are Built
One species, Smeagol manneringi, is quite small, growing up to 10 millimeters long. These slugs are blind and do not have tentacles. They are also very active.
All Smeagol species do not have a shell. They have a small, soft snout. Inside their mouth, they have a special tongue-like ribbon called a radula. This radula helps them scrape up food. They also have salivary glands that produce saliva.
These slugs breathe using a special lung-like structure called a pallial lung. They have an opening called a pneumostome that can open and close to let air in.
Where Smeagol Slugs Live
These slugs live in the upper intertidal zone on gravel surfaces. They are found in New Zealand and Australia.
The young Smeagol slugs develop completely inside their eggs. This means they hatch as tiny slugs and do not go through a larval stage where they swim freely.
- You can learn more about Smeagol slugs from a discussion on RNZ's Critter of the Week show, from 17 September 2015.

