Stellar precession facts for kids
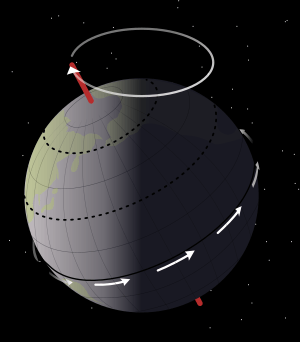
Stellar precession is a slow, gradual change in how the Earth spins. Imagine a spinning top that is slowing down and wobbling. The Earth does something similar as it spins. This wobble makes the stars appear to move slowly across the sky over very long periods.
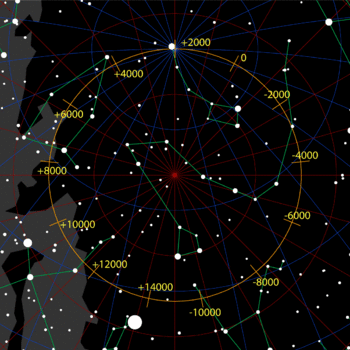
One of the most noticeable effects of this wobble is that the North Star changes over thousands of years. The star we call the North Star today won't be the North Star forever!
What Causes Precession?
The Earth's wobble is caused by the Sun's gravity pulling on our planet. The Earth's poles are not straight up and down compared to its orbit around the Sun. Instead, the Earth is tilted at an angle of about 23.42 degrees.
Because of this tilt, the Sun's gravity gently pulls on the Earth's bulge around its middle. This pull causes the Earth's axis to slowly point to different places in the sky. Think of it like a spinning top that is leaning over and its top point slowly draws a circle in the air. Even though the direction the Earth's axis points changes, the amount of its tilt stays the same.
How Long Does It Take?
It takes a very, very long time for the Earth's axis to complete one full wobble circle in the sky. This cycle takes almost 26,000 years!
Even though it's a long time, this movement has made a big difference in what star is seen as the North Star. For example, about 4,000 years ago, when the ancient Egyptians built the pyramids, they used stars to line up the pyramid edges with north and south. However, they did not use the same North Star that we do today. The Earth's North Pole pointed to a different star back then.
Who Discovered Precession?
Astronomers have known about this slow movement for a very long time. They often call it the precession of the equinoxes. Most people believe that a Greek astronomer named Hipparchus discovered it around 130 BC. However, some historians think that even the ancient Egyptians might have known about this celestial wobble.
Images for kids
-
Precession of a gyroscope