Sumatran short-tailed python facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sumatran short-tailed python |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Pythonidae |
| Genus: | Python |
| Species: |
P. curtus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Python curtus Schlegel, 1872
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Aspidoboa curta Sauvage, 1884 |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Sumatran short-tailed python (Python curtus) is a type of snake. It belongs to the Pythonidae family. This snake is not venomous, meaning it does not have poison. It lives naturally in Sumatra, an island in Southeast Asia.
Contents
About the Sumatran Short-Tailed Python
The Sumatran short-tailed python got its scientific name, Python curtus, in 1872. A scientist named Hermann Schlegel gave it this name. He described a python from Sumatra that had a very short tail.
What Does This Python Look Like?
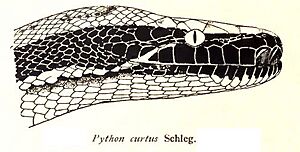
This python has special scales under its eyes. These are called subocular scales. They are narrow and sit between the eye and the upper lip scales. The scales on top of its head, called parietal scales, do not touch each other.
Adult Sumatran short-tailed pythons are quite large. They can grow to be about 1.5 to 1.8 meters (5 to 6 feet) long. They are also very thick and heavy-bodied snakes. As its name suggests, its tail is very short compared to its body length.
Their skin has a beautiful pattern. The main color is usually light brown, tan, or grayish-brown. On top of this, they have blotches that can be brick-red or even blood-red.
Where Do Sumatran Pythons Live?
This snake lives in several places in Southeast Asia. You can find it on the island of Sumatra. It also lives in the Riau Archipelago, Lingga Islands, and Bangka Islands. Other homes include the Mentawai Islands and parts of Kalimantan.
Python Habitats
Sumatran short-tailed pythons like to live in wet, warm places. They are found in rainforests and marshes. They also live in swamps and near rivers and streams. These areas provide good hiding spots and plenty of food.
What Do Sumatran Pythons Eat?
These pythons are predators. They hunt and eat different kinds of animals. Their diet includes various small mammals and birds.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Sumatran short-tailed pythons lay eggs. This means they are oviparous. Females usually lay about a dozen large eggs at a time. However, some females have been known to lay many more eggs.
The mother python stays coiled around her eggs. She protects them during the incubation period. This period lasts about 2.5 to 3 months. If the temperature gets too cold, below 32°C (90°F), she might shiver. This shivering helps to create heat for the eggs. But it uses a lot of her energy.
When the baby pythons hatch, they are quite small. They are usually about 30 centimeters (12 inches) long.
Sumatran Pythons and People
Some people keep Sumatran short-tailed pythons as exotic pets. Wild pythons can sometimes be unpredictable or aggressive. However, pythons born and raised by humans tend to be calmer.
These pythons have also been hunted for their skin. Their skin is used to make leather. It is estimated that about 100,000 of these snakes are taken each year for this purpose.
Images for kids




