Sushruta Samhita facts for kids

| Hindu texts |
| Śruti
Smriti |
The Sushruta Samhita is a very old Sanskrit book about medicine and surgery. It is one of the most important books on these topics that we still have from ancient times. This book is also called the Compendium of Suśruta.
It is one of the main books for Ayurveda, which is a traditional Indian medicine system. Other important books include the Charaka-Saṃhitā and the Bhela-Saṃhitā. The Sushruta Samhita is special because it has unique chapters about how to train for surgery, what tools to use, and how to do operations. Many of these ideas are still used in modern surgery today.
One of the oldest copies of the Sushruta Samhita is a palm-leaf manuscript. It is kept safe at the Kaiser Library in Nepal.
Contents
When Was the Sushruta Samhita Written?
For a long time, experts have tried to figure out exactly when the Sushruta Samhita was written. It's tricky because the book seems to have been put together by different people over many years.
Early Ideas on the Date
More than a hundred years ago, a scholar named Rudolf Hoernle thought the book might be from around 600 BCE. He based this on other ancient texts that seemed to know about Sushruta's ideas. Many people still use this date, but newer studies show it's more complicated.
Modern Views on the Book's Age
Today, most scholars believe the Sushruta Samhita was created in several steps. The first parts might have been written in the last few centuries BCE. The book was then finished in its current form by another author who added a long final section called the "Uttaratantra." This final version was likely completed by 300-500 CE.
So, it's not just one author or one date. It's a collection of knowledge that grew over time.
Who Wrote the Sushruta Samhita?
The book itself names Sushruta (which means "well heard" or "renowned") as the author. Later copies say that Sushruta was teaching what his guru, Divodāsa, had taught him.
Some old texts, like the Buddhist Jataka tales, mention a physician named Sushruta. He is said to have taught medicine in a school in Kashi (now Varanasi) a very long time ago.
Many experts believe that several ancient authors named "Sushruta" helped write this text. It's like a big project that many smart people worked on over generations.
What Is the Sushruta Samhita About?
The Sushruta Samhita is one of the most important ancient medical books. It is a key text in India's medical history.
What Topics Does It Cover?
The Sushruta Samhita covers many topics, just like another important Indian medical book, the Caraka-Saṃhitā. Both books talk about:
- General rules of medicine
- How diseases develop
- How to diagnose illnesses
- Human anatomy (the body's structure)
- How to predict what will happen to a patient
- Treatments and medicines
- How to make medicines
- Poisons and how to treat them
The main difference is that the Sushruta Samhita focuses a lot on surgery, while the Charaka Samhita is more about general medicine.
How Many Chapters and Illnesses?
The Sushruta Samhita has 186 chapters. It describes:
- 1,120 different illnesses
- 700 medicinal plants
- 64 preparations made from minerals
- 57 preparations made from animal sources
The book is split into two main parts. The first five books are thought to be the oldest. The last part, called the "Later Section" (or Uttaratantra), was added later.
Preventing Illnesses
Sushruta believed that doctors should try to prevent diseases as much as they try to cure them. He said that physical exercise and good hygiene are very important for prevention.
However, he also warned that too much exercise can be harmful. He suggested that regular, moderate exercise helps your body fight off diseases and stay healthy.
Human Bones
The Sushruta Samhita talks about the human skeleton. It says there are 300 bones in the body. It lists them like this:
- 120 bones in the arms and legs
- 117 bones in the pelvis, sides, back, stomach, and chest
- 63 bones in the neck and head
This shows that ancient Indian doctors carefully studied the human body.
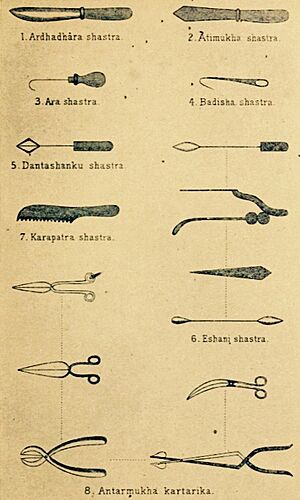
Surgery in Ancient India
The Sushruta Samhita is most famous for its detailed discussions about surgery. It was one of the first books in history to suggest that students learning surgery should study the human body by dissecting (carefully cutting open) a dead body.
The text also said that students should practice on things that are similar to body parts. For example, to learn how to make cuts, they could practice on:
- Squash or gourds
- Leather bags filled with liquids
- Bladders from dead animals
The book describes many types of operations, such as:
- Removing hemorrhoids
- Amputations (removing a limb)
- Plastic surgery (like fixing a nose)
- Eye surgeries
- Removing bladder stones
- Procedures for childbirth
The Sushruta Samhita talks about different ways to do skin grafts, like moving a piece of skin from one part of the body to another.
Medicinal Plants
Along with other ancient Indian medical books, the Sushruta Samhita describes more than 700 medicinal plants. It tells you about their taste, how they look, how they affect digestion, and how safe and effective they are. It also gives advice on how much to use.
Nose Reconstruction (Rhinoplasty)
Rhinoplasty, often called a "nose job," is surgery to:
- Help someone breathe better through their nose.
- Improve the look of the nose.
The Sushruta Samhita has the first written record of a cheek flap rhinoplasty. This is a technique where a piece of skin from the cheek is used to rebuild a nose that has been cut off. This method is still used today! The book describes more than 15 ways to repair a nose.
In ancient India, the nose was a symbol of dignity. Losing one's nose was a common punishment. So, reconstructive surgery offered hope for people to live normal lives again. This need helped the practice of rhinoplasty grow into a full science.
Copies and Translations
The first printed version of the Sushruta Samhita was made in Calcutta in 1835. The first full English translation was published in three volumes between 1907 and 1916 by Kaviraj Kunjalal Bhishagratna.
Many of the printed versions of the book are based on only a few of the hundreds of old copies that still exist today. Experts are still working to create a complete and perfect version of the Sushruta Samhita by studying all the different manuscripts.
See also
 In Spanish: Susruta-samhita para niños
In Spanish: Susruta-samhita para niños
- Ayurveda, Indian traditional medicine
- Hindu texts, Indian religious literature
- On Ancient Medicine, a Greek medical text from around 450–400 B.C.
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |