Toughness facts for kids
Toughness is how well a material can soak up energy and change its shape without breaking. Think of it like a superhero's shield: it can get hit hard and bend a little, but it won't shatter. Toughness shows how much force a material can handle before it breaks apart.
When we talk about toughness, we mean the amount of energy a material can absorb in a certain space before it breaks. This is different from "fracture toughness," which is about how well a material stops cracks from spreading. For a material to be tough, it needs to have a good mix of being both strong and stretchy (this stretchiness is called ductility).
Contents
What Makes a Material Tough?
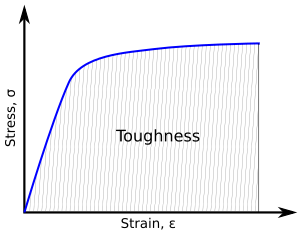
Toughness is linked to something called the stress–strain curve. Imagine you're pulling on a rubber band. The "stress" is how much force you're putting on it, and the "strain" is how much it stretches. The area under this curve on a graph tells us how tough the material is.
To be tough, a material must be both strong and ductile.
- Strong means it can handle a lot of force without breaking.
- Ductile means it can stretch or bend a lot without breaking.
For example, a ceramic plate is strong, but it's not very ductile. If you drop it, it shatters easily because it's not tough. On the other hand, a very soft piece of clay is ductile (it can change shape a lot), but it's not strong. It won't break, but it also can't hold much weight. A tough material can handle both high forces and big changes in shape before it breaks.
Measuring Toughness
Scientists can measure a material's toughness using special tests. One common way is to use a machine with a swinging arm, like a pendulum. They take a small piece of the material, often with a notch cut into it, and hit it with the pendulum.
By measuring how high the pendulum swings after hitting the material, they can figure out how much energy the material absorbed. If the material absorbs a lot of energy, it means it's tough. The Charpy impact test and Izod impact strength test are two well-known tests used to find out how tough a material is.
Units of Toughness
Toughness is measured in units of energy per volume. In the SI system (the international system of units), toughness is measured in joules per cubic metre (J·m−3). This makes sense because toughness is about how much energy a material can absorb in a certain amount of space before it breaks.
You can think of it like this:
- Energy is measured in Joules (J).
- Volume is measured in cubic metres (m3).
- So, toughness is J/m3.
The Toughest Material Discovered So Far
Scientists have found that an alloy (a mix of metals) made of almost equal parts of chromium, cobalt, and nickel (called CrCoNi) is the toughest material known. What's amazing is that it stays incredibly tough even in super cold temperatures, almost as cold as absolute zero! This makes it a very promising material for building things like spacecraft that need to withstand extreme conditions.
See also
 In Spanish: Tenacidad para niños
In Spanish: Tenacidad para niños
- Hardness
- Shock (mechanics)
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |