Mutation facts for kids
In biology, a mutation is a change in an organism's genetic material. This means changes to the DNA or to the chromosomes that carry the DNA. These changes can be passed down to the next generation, unless they are so harmful that the organism cannot survive.
Mutations can happen for different reasons. Sometimes, mistakes happen when cells divide to make eggs or sperm (a process called meiosis). Also, damage from radiation or certain chemicals can cause mutations. Mutations happen by random chance.
Sometimes, an individual carrying a mutation is called a mutant. The new trait or feature caused by the mutation can also be called a mutation.
Contents
Types of Mutations
DNA Changes
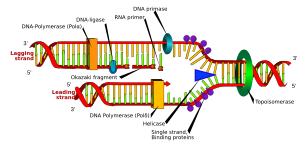
When DNA is copied, mistakes can sometimes happen. These mistakes are called mutations. There are four main types of DNA mutations:
- Deletion: One or more DNA building blocks (called bases) are left out.
- Insertion: One or more extra bases are added into the DNA sequence.
- Substitution: One or more bases are swapped for different ones in the sequence.
- Duplication: Whole genes are accidentally copied, making extra copies.
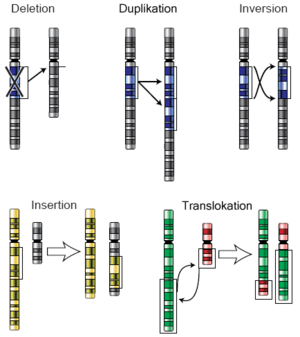
Chromosome Changes
These mutations involve larger changes to the chromosomes themselves. The second image in this article helps explain these terms:
- Deletion: A piece of a chromosome is lost. Any genes on that lost piece are also gone.
- Duplication: A part of a chromosome is repeated, so there are extra copies of that section.
- Inversion: A section of a chromosome gets flipped around, so it's in reverse order.
- Insertion: A piece from one chromosome gets added into another chromosome.
- Translocation: A part of one chromosome breaks off and moves to a completely different chromosome.
What Happens Because of Mutations?
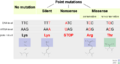
Mutations can have different effects on an organism. They can be harmful, have no effect, or even be helpful. Sometimes, a mutation is fatal, meaning the organism cannot survive. This happens if the new protein made by the changed DNA doesn't work at all, causing the embryo to die.
On the other hand, mutations are very important for evolution. When a new version of a protein works better for an organism, it can help that organism survive and reproduce.
Mutations are the original source of variation in living things. This variation is what natural selection acts upon. Some mutations affect an organism's ability to live and have offspring. This is a key part of the theory of evolution. The amount of variation that can be passed down through generations can be huge. Because of this, populations of organisms can change and adapt to new conditions in their environment.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
A red tulip with a partially yellow petal due to a mutation in its genes.
-
Prodryas persephone, an ancient butterfly from the Late Eocene epoch.
-
A covalent adduct between a chemical from tobacco smoke and DNA.
-
Dutch botanist Hugo de Vries painting an evening primrose, a plant that showed new forms in his experiments.
See also
 In Spanish: Mutación para niños
In Spanish: Mutación para niños