Treaty of Schönbrunn facts for kids
The Treaty of Schönbrunn was an important agreement signed between France and Austria on October 14, 1809. It was signed at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna. This treaty officially ended the War of the Fifth Coalition, which was part of the larger Napoleonic Wars. Austria had been defeated by France in a major battle called the Battle of Wagram just a few months earlier.
Why the Treaty Happened
During the Peninsular War in Spain, where the Spanish people fought against Napoleon, Austria tried to get back lands it had lost earlier. Austria also tried to start rebellions against Napoleon's control in Central Europe, like the Tyrolean Rebellion.
However, these efforts did not work. French forces took over Vienna in May 1809. The Austrian army, led by Archduke Charles, managed to win a battle at Aspern in May. But Napoleon's army came back stronger and defeated Archduke Charles's army at Wagram. After this defeat, Austria had to agree to a ceasefire.
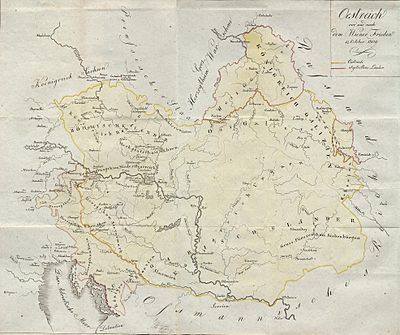
What the Treaty Said
France set very strict rules for Austria in the treaty. Austria had to give up a lot of its land:
- The Duchy of Salzburg went to Bavaria.
- Austria lost its way to the Adriatic Sea. This included areas like Gorizia and Gradisca, Trieste, Carniola, Istria, and parts of Carinthia and Croatia. These lands became part of the French Empire, known as the Illyrian Provinces.
- West Galicia was given to the Duchy of Warsaw.
- The Tarnopol district went to the Russian Empire.
Austria also had to agree that Napoleon's earlier wins were valid. They also had to accept Napoleon's brother, Joseph Bonaparte, as the King of Spain. Austria also had to pay a large amount of money to France. The Austrian army was supposed to be made much smaller, but this rule was not fully followed. The Schlossberg fortress in Graz, which had bravely fought against the French, was mostly destroyed.
Austria also had to join Napoleon's "Continental System." This system was a blockade meant to stop trade with Britain, which was still at war with France.
Even though Austria lost a lot, it remained a powerful country in Europe. To improve relations with France, Austrian Emperor Francis I allowed his daughter, Marie Louise, to marry Napoleon in 1810. Later, Austrian forces even joined Napoleon's army when he invaded Russia in 1812.
Assassination Attempt on Napoleon
During the peace talks at Schönbrunn, someone tried to kill Napoleon. On October 12, 1809, just before the treaty was signed, Napoleon was leaving the palace. A 17-year-old boy named Friedrich Staps tried to get close to him. Staps was the son of a pastor.
Napoleon's aide, General Jean Rapp, noticed Staps acting suspiciously. He had Staps arrested. When searched, Staps was found to have a large knife hidden in his coat. Staps openly admitted he planned to kill Napoleon, saying Napoleon was bad for his country. When Napoleon asked if Staps would be thankful if he was pardoned, Staps replied, "I would kill you nonetheless."
Napoleon left Vienna on October 16. The next day, Staps was executed by a firing squad outside the palace. He is said to have shouted, "Long live freedom! Long live Germany!" Napoleon was surprised by this event and wanted to keep it a secret, fearing a bigger plot.
Later, Staps became known as a hero for German nationalism. He was even the subject of a poem and a play.